Set up relationships in DocGen Packages
Relationships are associations between objects Salesforce says, "An object allows you to store information in your Salesforce organization." that retrieve data that you can use in the documents you generate. Different types of relationships between objects in Salesforce determine how they handle data deletion, sharing, and required fields in page layouts.
|
|
To watch video tutorials on how to use this Nintex capability, take the Certification: Nintex Document Generation Expert - Nintex DocGen for Salesforce in Nintex University. |
What can you do with relationships?
Relationships send the data within objects to your DocGen Packages A customizable package that consists of your Salesforce data, documents, and delivery configurations for documents you want to generate. to create documents. The Field Tagger shows tags A prefilled word block that DocGen selects for fields in your DocGen Package. The tag is a placeholder for the value being retrieved from Salesforce and it gets replaced with the relevant information when the document is generated. that represent what data is available for that DocGen Package.
You can use relationships to:
-
Alias data so that you can identify tags or isolate data from a particular relationship in the Field Tagger A tool that displays tags for your template based on the object you're working with and easily inserts the field tags into your templates for your DocGen Package..
-
Filter data so that tags only produce certain data in output documents.
-
Replicate data with repeat by options to build tables, groups of tables, or duplicate entire sections of your document, with unique data in each section.
Types of relationships
There are five different types of relationships. You can combine relationship types to get the required data for your DocGen Packages.
| Relationship Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Relationships from Starting Objects | Starting Object relationships are known as the basic relationships. We recommend you use this option first. |
| Set up relationships from other objects in DocGen Packages | Relationships from Other Objects are similar to Salesforce Objects except they can start with any standard object rather than just the starting object for the DocGen Package. Use these when you want to create a relationship from an additional standard object Objects that are in a Salesforce org by default e.g. Account, Contact, Lead, Opportunity.. |
| Stand Alone Data Relationships | Use Stand Alone Data relationships to include data from objects that do not need or have a direct link to other objects in your DocGen Package. |
| SOQL Query Relationships | SOQL Query Relationships are perfect for users who are comfortable with SOQL or if there is a complex relationship that would be hard to express using another relationship type. |
| Apex Data Relationships | Apex Data Relationships are perfect for users who are comfortable with Apex. You can extract and process data in one step. |
Supported relationships
The following supported relationships can be created within your DocGen Package with these relationship types.
| Relationship type | Supported relationship | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Lookup relationships |
Can only be created from the first parent object in Relationships from Starting Objects or Relationships from Other Objects. |
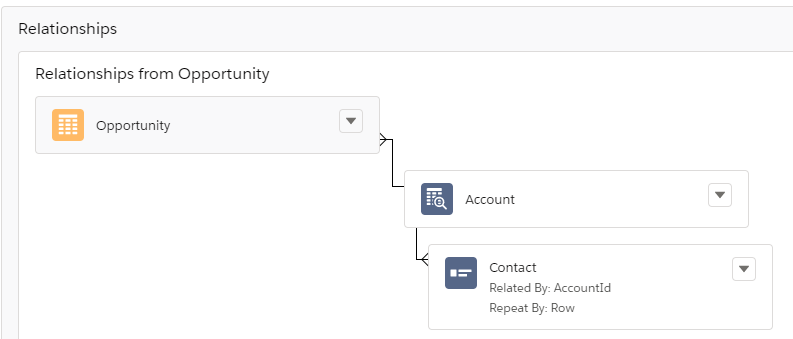
Opportunity is the parent starting object and the Account is the lookup relationship.
|
| Child relationships |
Can be created from:
|
The Parent Object, which is also the Starting Object in this DocGen Package is Account, and the child relationships are Opportunity, Quote, and Quote Line Item. 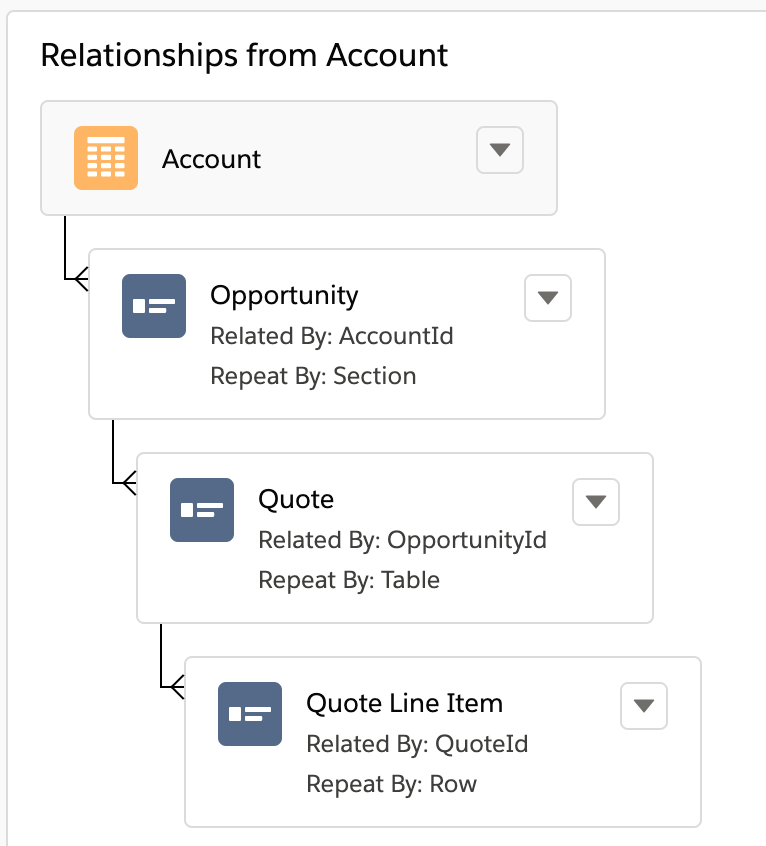
|
Relationship Limits
30,000 Row Limit
- There is a maximum of 30,000 rows of data allowed from all relationships combined.
Repeat By Limit
Each Repeat By option has their own limits. You can use repeat by options to build replication tables, groups of tables, or duplicating document sections. See the table below for details on Repeat By options and their supported template types, and relationships.
| Repeat By options and descriptions | Supported template type(s) | Supported relationships | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Section: Allows the data from the Relationship to be represented as sections within Microsoft Word. | Word | All except Other Objects | |
| Table: Allows the data from the Relationship to be presented in tables. Each table has unique data. | Word, PowerPoint (Slide Replication) | All except Other Objects | |
| Row: Allows the data from the Relationship to be presented in rows that have unique data in each row. | Word, PowerPoint, PDF/Excel | All except Other Objects | |
| Group: Duplicates tables that are grouped by field type. | Word, PowerPoint |
Starting Objects (only from parent relationships) |
|
| Hierarchy: Creates slides with a levels of relationships based on field type. | Word, PowerPoint |
All except SOQL Query and Other Objects |
Supported Repeat By combinations
|
|
|
|
Common relationship fields
Many relationships use the same fields (for example, Alias) when creating or managing relationships. The table below shows common fields shared between relationship types:
| Section | Field |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Information | Alias |
This field helps you differentiate filtered relationships from one another. Also, a new tag is created using the name you enter for the Alias field. Alias Requirements:
Important: This applies to all current and future objects that you create.
Example: Namespace__ObjectName__c would be stripped to ObjectName; therefore, you cannot have an alias of ObjectName. |
|
| Repeat By |
Determines how records within your related object will be merged into your document.
|
||
| Delete Table, Chart, Section (if no records) | The entire table/chart/section will be deleted if your related object contains no records Salesforce says, "A single instance of a Salesforce object. For example, “John Jones” might be the name of a contact record.". | ||
| Order By Criteria | Unnamed Drop-down box |
Specifies the field which determines the order in which your related object records will be inserted into the document. Based on the field selection, the records are sorted alphabetically within your related object. If None is selected, records are sorted by Name. |
|
| Add field | A new field is added to order fields by. | ||
|
|
Ascending |
Specifies the field should use ascending order. |
|
| Descending | Specifies the field should use descending order. | ||
| Filter By Criteria | Numbered filter rows | Enter field criteria. You must enter a field on your related object to filter by, a criteria and a value. You can have one to several filters on a relationship. | |
| Field | The field that is getting filtered. | ||
|
|
Operator |
Determines how the field and value will be filtered. |
|
|
|
Value |
The keyword used by the operator to filter the data. |
|
|
|
|
Removes a filter line. |
|
|
|
Add Filter | A new filter row will be added. |
|
|
|
Advanced Filter |
Refines filter by using Boolean logic expressions in Advanced Filter Conditions. For more information, see Add Filter Logic in the Salesforce documentation. |
|
Filter a relationship
You can use filters in a relationship so tags that are generated from that relationship will only show the filtered information.
For example, say you want to connect a custom object Salesforce says, "Custom records that allow you to store information unique to your organization." to a standard object Objects that are in a Salesforce org by default e.g. Account, Contact, Lead, Opportunity. using a Starting Object relationship, but you only want certain details from your custom object to appear in the output.
Some filters are only available for some relationships, while others have limitations.
| Relationship | Description |
|---|---|
| Starting Object | This is an optional field. Filtering is only available for child relationships. |
| Other Objects | This is an optional field. Filtering is only available for child relationships. |
| Stand Alone Data | This is an optional field. Filtering is only available for child relationships. |
| Apex Data | This is an optional field. |
| SOQL Query | Filtering for SOQL Query relationships is done in the SOQL query. |
- Navigate to the App Launcher by selecting
 in the upper left corner and select Nintex DocGen.
in the upper left corner and select Nintex DocGen. - Select the DocGen Packages tab.
- Open the DocGen Package you want to filter.
- In the Relationships window, create a new relationship based on the type of relationship you want to create.
- For more information on how to create a relationship, see Types of relationships.
- Select the drop down arrow
 next to the object you want to filter.
next to the object you want to filter. - Click Add Child +.
- Select the standard Object you want to create the relationship for.
- Select the Related By option:
- None: Always available and resets the user interface.
- Lookup from what you have: This option is dependent on the object you selected.
- This field is optional. In Alias, type in a short name or keyword that will differentiate a relationship to identify the tags A prefilled word block that DocGen selects for fields in your DocGen Package. The tag is a placeholder for the value being retrieved from Salesforce and it gets replaced with the relevant information when the document is generated. from that relationship in the field tagger. Enter Repeat by options.
Default value is Row.
- Click + Add Filter.
- Select the Field, Operator, and Value you want to filter your relationship.
- For example, say you want to filter your relationship to show a list containing only contacts with the name Bob.
- You would input the following:
- Field: Name
- Operator: is equal to
- Value: Bob
- You can use the Advanced Filter for Boolean logic expressions to refine your filter even further.
- Click Save.
- Navigate to the App Launcher by selecting
 in the upper left corner and select Nintex DocGen.
in the upper left corner and select Nintex DocGen. - Select the DocGen Packages tab.
- Open the DocGen Package you want to filter.
- Navigate to a child relationship that is already linked to the master object and click Edit
 .
.
- Click + Add Filter.
- Select the Field, Operator, and Value you want to filter your relationship.
- For example, say you want to filter your relationship to show a list containing only contacts with the name Bob.
You would input the following:
- Field: Name
- Operator: is equal to
- Value: Bob
- You can use the Advanced Filter for Boolean logic expressions to refine your filter even further.
- Click Save.
Build tables, group tables, or duplicate document sections
Replicate data with copy types to build tables, group tables, or duplicate entire sections of your document, with unique data in each section.
Copy Types
The table below shows each copy type and why you would use that particular copy type.
| Copy Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Section | Duplicate an arbitrary section of your document, with unique data in each section. |
| Table | Duplicate tables, with unique data in each table. |
| Row | Duplicate rows, with unique data in each row. |
| Group | Duplicate tables grouped by a particular field type. For more information, see Group data in tables. |
| Hierarchy | Create slides with a hierarchy of relationships based on a particular field type. |
Copy Type limitations
Copy Types are not supported across every relationship or template type. Some templates don't support certain combinations of Copy Types.
| Copy Type | Templates types | Sales relationships |
|---|---|---|
| Section |
|
|
| Table |
|
|
| Row |
|
|
| Group |
|
|
| Hierarchy |
|
|