Send Value
The Send Value action An instruction within a botflow. sends a value to a target An element within an application Nintex RPA LE interacts with, such as a button, text field, or checkbox., such as a text box. Using this action, you can:
- Send text data to a text editor.
- Send shortcut keys to a target.
- Send a Ctrl+C command to copy information.
Some examples of target applications for the Send Value action using the Target Selector are:
- Microsoft Excel spreadsheet cells.
- Nintex Forms.
- Browser windows.
Jump to:
Add a Send Value action to a botflow
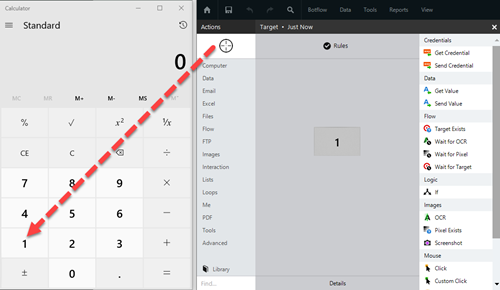
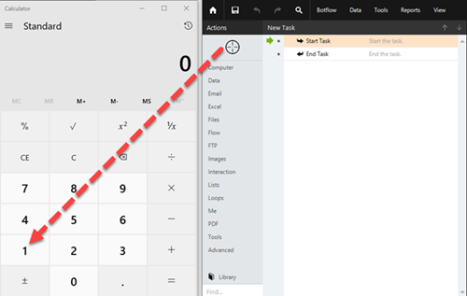
- Drag the Target Selector from the Build Pane Area to add new actions and edit existing actions. The Build Pane displays after you select a targeted element in a Windows application. The center of the Build Pane is referred to as the Task Editor Pane. and drop it onto an application to display the Target Preview.
- Select Send Value from the Data actions list.
- Enter the value to Send to the target application.
- Hide Value: Hides the sent value.
- Bypass the keyboard: This setting displays when the target resides in a browser window.
- Click before sending: Clicks the target before sending the data to the target.
- Tab after sending: Sends a Tab command after the value is sent.
- Change case: Changes the sent value to Upper, Lower, or Proper case.
- Remove spaces: Removes Leading, Trailing, or All spaces from sent values.
- Mode: Sets the mode of the sent value.
- Speed: Sets the speed of the sent value.
- Keystroke delay: Sets the automatic delay of the speed of the keyboard in milliseconds.
- Use Virtual Key Codes: Allows the application to receive the physical key on which a user strikes on the keyboard to produce the results on the screen.
- If needed, adjust the Rule settings to modify how Nintex Bot finds the application target.
See the Send Value settings for more information about:
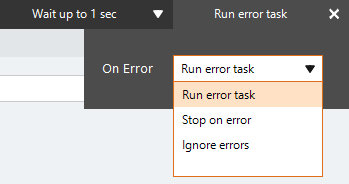
- If needed, adjust the Run Error Task settings and Timing settings to fine tune how the action runs.
- View the action Details settings.
- If needed, adjust the Run Switch setting to create the action without running it.
- (Optional) Add an action note.
- Click OK to add the Send Value action to the botflow Automated steps that you can design for each bot that will run..
Send Value Action field and button descriptions
| Field or button | Description |
|---|---|
| Target Selector |
The Target Selector allows you to choose the target element the botflow interacts with, such as a button, text field, or check box. Ensure that your machine's Windows Settings (Start Menu > Settings) are set as follows when using the Target Selector:
You can use the Target Selector to:
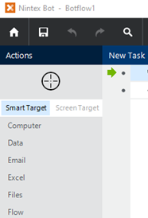
Drag the Target Selector from the Task Pane onto the desired application target An element within an application Nintex RPA LE interacts with, such as a button, text field, or checkbox. and select the appropriate action from the Build Pane Area to add new actions and edit existing actions. The Build Pane displays after you select a targeted element in a Windows application. The center of the Build Pane is referred to as the Task Editor Pane.. Smart Target and Screen Target options The Target Selector can be used with the Smart Target or Screen Target options. The options are displayed as shown in the image below. Smart Target is selected by default.
|
| Build Pane |
The Build Pane displays after you select a targeted element in a Windows application. In the Build Pane, you can:
Selected target elements display in the Build Pane with a list of actions supported by the targeted item. The Build Pane also displays how long the item has been targeted.
|
| Recent Target |
Access the most recent target by clicking the Recent Target button to the right of the Target Selector.
This is useful when creating Excel, Emulator, and Web Table Targets, allowing you to create new actions with existing targets. |
| Field or button | Description |
|---|---|
| Send Value Options/Settings | General
Note: Nintex Bot sends data to a field using the keyboard. Bypass the keyboard sends the information without the physical keyboard. Some applications only respond to changes submitted by an actual keyboard. These applications will not support Bypass the keyboard. To determine if your target application supports this feature, perform the action and confirm that changes have been made. Format
Keystrokes
Preview: Shows the exact value that will be sent to the target. |
| Rules |
Some actions have rules required to locate a target and vary based on the targeted application. Rules of a targeted application element are configured and saved with the action. The rules are then used to locate the proper targeted element, such as a Microsoft Excel workbook. Other notes about rules:
To set up the most common rules:
The Rules window displays the rules available for the selected targeted application. |
| Preview | All actions created using the Target Selector include a preview of the targeted element. |
| Details |
When directed by Nintex Support, click Details from the Preview Panel of the Action Builder. If needed, Nintex Support will supply additional information. |
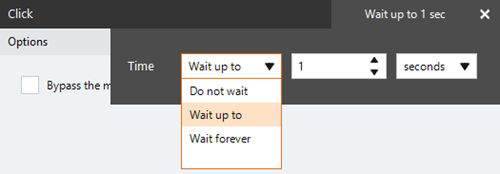
| Timing Settings |
Some actions have timing settings and vary based on the targeted application. The timing settings of a targeted application element are configured and saved with the action. The timing settings are then used to control when the action starts.
|
| Run error task |
|
| Note |
(Optional) Type a Note to document any special instructions or functionality.
|
| Run Switch |
The Run Switch toggle controls how Nintex Bot runs an action when adding or editing an action in a botflow.
|
| OK/Cancel | Click OK to save the action or click Cancel to discard the action or any changes. |