Managing Processes and Process Instances with the legacy K2 Workspace
Recall that workflows are known as Processes in K2 and Process Instances are a single occurrence of a Process. Throughout this tutorial, both sets of terms will be used. Just know that Workflows are Processes, and Workflow Instances are Process Instances. The tools most commonly used for administering and managing processes, are Process Rights (or assigning permissions to a Process), Versions (which allow the administrator to change the default workflow version used in a Process) and Instances (where the administrator can stop, start and remove Process Instances). In this part, we will explore all three tools and observe the results after we have made changes.
As a precursor to our tutorial steps, we need to generate several process instances of the Workflow Administration Sample Process. In the real world, new process instances are most likely created when a user submits a form (and starts the workflow). Because we are not working with forms, we will start process instances from K2 Workspace. You could also use this tool for testing and troubleshooting your workflows without having to open and submit forms.
Step 1 Tasks
- Start six instances of the Workflow Administration Sample process, using the following entries for each Folio parameter.
- Task Redirect
- GoToActivity
- Start Stop
- Deleted
- Normal Execution 1
- Normal Execution 2
- Launch K2 Workspace, and then click Instances found under the Workflow Administration Sample Process. (If you do not know where to access K2 Workspace, ask your K2 administrator for the URL to your K2 workspace site)
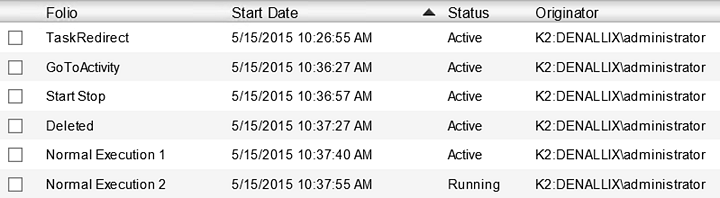
- We need to create several more process instances for future tutorial steps. Using the same steps as above, Start New Process Instances using the following entries for each Folio property:
- GoToActivity
- Start Stop
- Deleted
- Normal Execution 1
- Normal Execution 2
The Instances screen opens in the central pane. Notice there are no Instances shown. This is telling you that this Process (Workflow Administration Sample) does not have any active process instances at this time. It could be a newly deployed process, or simply mean that any process instances for this workflow have completed or have been removed.
Click the Start New button found in the menu bar. On the Create new Process Instance screen, notice the Folio field. The Folio is a unique identifier that allows the administrator to differentiate one process instance from another. By default, K2 assigns the date for the Folio when starting process instances from K2 Workspace. We are going to enter our own Folio properties, which will allow us to pick and choose different process instances for our tutorial steps.
UNCHECK the Use Date box. In the Folio field, enter
TaskRedirect
then click Start.
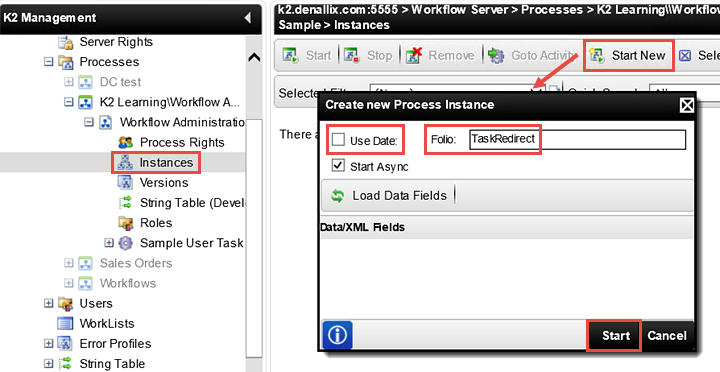
Notice now, we have one active 'Workflow Administration Sample' Process Instance. Notice too, the Folio value is the TaskRedirect property we just entered. The Running status indicates that K2 is actively processing this workflow, if you refresh the list you should see the status change to Active which means that the workflow is active and waiting for input, in this case for a user to complete a task.
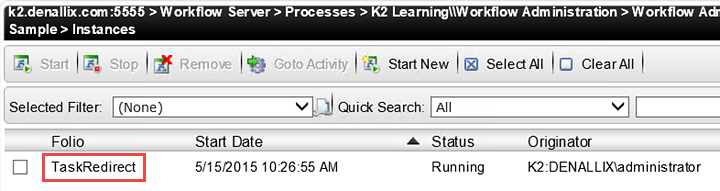
Your screen should now look like the image below. When first started, process instances show a Running Status value, which then updates to Active, wherein the workflow is now waiting for the next workflow step to take place. The Instances screen also shows us who started the workflow (Originator) and when it was started.
STEP 1 REVIEW
In this step, we started a number of process instances from the Workflow Administration Sample Process. We set the Folio property for our process instances using manually entered values. In the real world, you will likely assign a form field value as the Folio during the workflow build (such as the form originator's name or any other key value from the form). The Folio is not a required value and there are some instances where you will not assign any value (leaving it blank). Because it helps make each process instance unique from other process instances, administrators will find that using the Folio is a must-have value!
Now, we will use the Instances tool to pause ("stop"), then resume ("start") a process instance. There are number of reasons why you might want to stop, or suspend a workflow. One example might be the workflow is currently waiting for a user to action a task of some kind. Suppose that user is unavailable and will be for a long period of time. If it's not feasible to redirect the task to another user, you might just stop it, then restart it when the user is once again available. Or perhaps you have workflows that need to query some external system that will be offline for a while. To prevent errors, you can pause these workflow instances until that system is back online and then resume the workflows. Stopping workflows suspends all workflow tasks (system and user), then immediately starts those tasks up again when the process instance is restarted. In this step, we will also remove a process instance.
Step 2 Tasks
- Stop, then Start, the Start Stop Folio Process Instance, observing the Status values after each action.
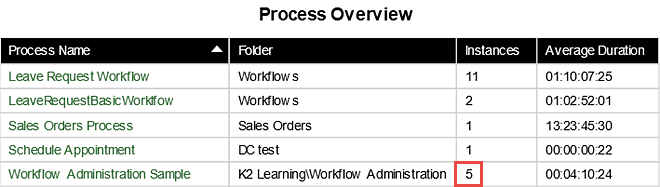
- Open the Process Overview Report and confirm you can see the Deleted Process Instance for the Workflow Administration Sample Process.
- Returning to the Instances tool, Remove the Deleted Process Instance. Be sure to CHECK the box to Remove the logs as well.
- Open the Process Overview Report, then confirm that the Deleted Process Instance is no longer shown.
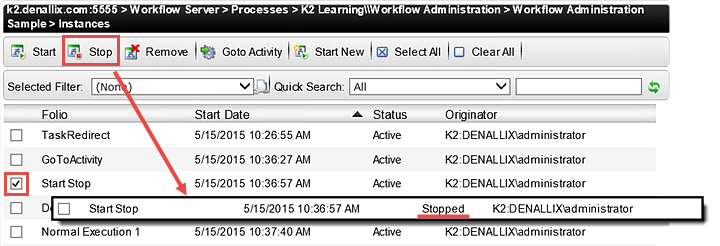
- In the Instances management pane, CHECK the box to the left of the Start Stop Folio Process Instance to select it. Click the Stop button found in the navigation pane. Notice the Status value after you have stopped the instance.
- Select the Start Stop Process Instance once again and Start it. Notice the Status value.
- Click the Home icon in K2 Workspace to return to the landing page. Once on the landing page, click the Process Overview Report link found in the Reports pane. (It may take a while for the report to open depending on your environment.)
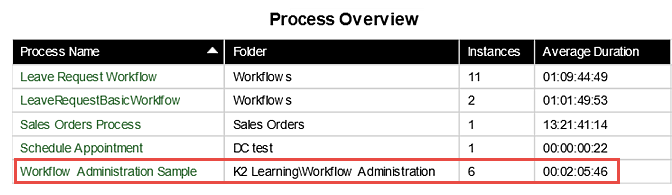
- When the Process Overview Report opens, you will first see a list of all processes that have been deployed, along with the number of process instances that have been started for each process. Notice the Workflow Administration Sample Process indicates the 6 instances we started in the previous steps. Click on the Workflow Administration Sample Process to drill-down into its Process Instances report.
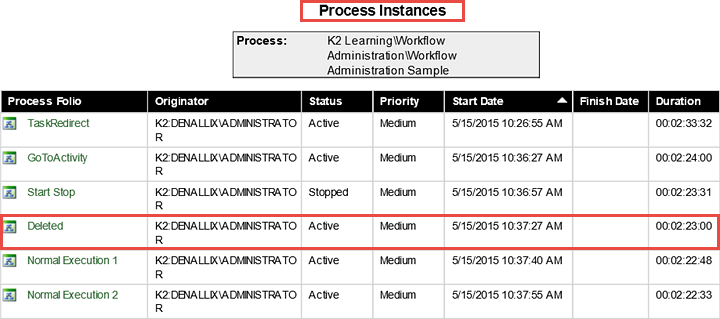
- On the Process Instances screen you will see a list of all the instances for this process. This list will include instances that are currently active, as well as instances that historical (completed). Confirm that the Deleted Process Instance is shown and is currently Active.
- Click the Home icon in K2 Workspace to return to the landing page. Open the Management Console and navigate to the Workflow Administration Sample Process. (Management Console > K2 Server > Workflow Server > Processes > K2 Learning\Workflow Administration > Workflow Administration Sample) Open the Instances pane.
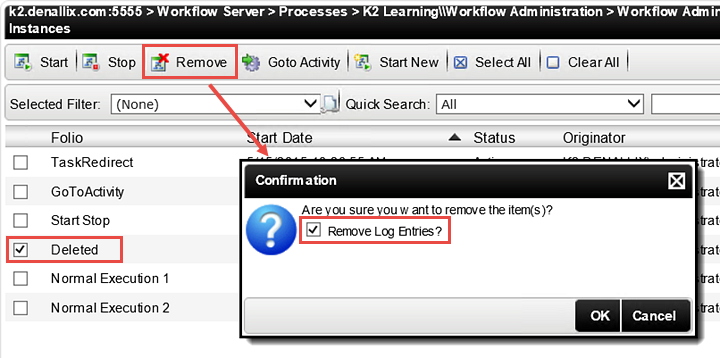
- CHECK the box to select the Deleted Process Instance, then click Remove.
- Click the Home icon in K2 Workspace to return to the landing page. Click the Process Overview Report in the Reports pane. Confirm that the Instance total for the Workflow Administration Sample is now 5, instead of 6.
- Click the Workflow Administration Sample Process to drill down into the Process Instances. Confirm the Deleted Process Instance is no longer there.
Now we are going to remove a process instance, which will permanently delete it from K2. (You cannot retrieve a deleted process instance if you have removed it) To demonstrate this, we will first open the Process Overview Report and observe the Deleted Process Instance's current workflow step. The Process Overview Report contains current, as well as historical data for process instances. (To learn more about the Process Overview Report, access the Reporting in K2 tutorials.)
Now we will return to the Management Console and remove the Deleted Process Instance from the Instances management screen. Once deleted, we will return to the Process Overview Report and confirm the instance is no longer shown.
Here is an example of why you might want to remove a process instance. Say you have a user that has submitted a workflow and the workflow is currently waiting approval from some destination user. The originator decides at some point they want to cancel the workflow (and hopefully after having informed the destination user they are canceling), they ask you if you can delete the workflow. You can accomplish this by removing the process instance. This is also another example of how the Folio might be very helpful in locating the correct process instance to remove, if there are many.
You will now see a confirmation pop-up. In the Confirmation pop-up, CHECK the box to Remove Log Entries, then click OK. Removing the log entries completely deletes the process instance and any related records from K2.
The Deleted Process Instance should no longer be shown on the Instances screen. To confirm the process instance has been completely removed from K2, let's return to the Process Overview Report. Recall that the Process Overview Report shows all Process Instances, whether they are active or not.
STEP 2 REVIEW
In this step, we stopped, or suspended, the Start Stop Process Instance. Stopping a process instance does not remove it, it merely puts in 'on hold' until the instance is either started or removed. If there are any tasks that have been fired off when the instance was stopped, they will immediately fire off again when the instance is started. To permanently delete a process instance from K2, choose the Remove option, making sure to select the Remove Logs option as well. Once you remove a process instance and its logs, there is no way to retrieve it.
In this step, we will choose the GoTo Activity option to send a process instance to another workflow step. For example, suppose a user has submitted a workflow. They contact you at some point to say they need to make a change to their form entry and want to know if there is any possibility of retrieving the form/workflow. This can be accomplished by using the GoTo Activity option. The GoTo Activity allows you to send the process instance to any of the steps in the workflow.
Step 3 Tasks
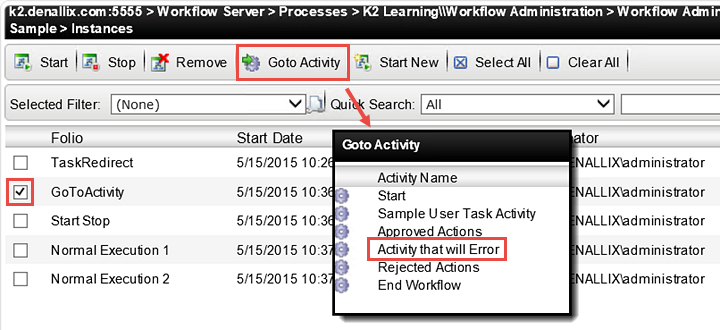
- Using the GoTo Activity option, redirect the GoToActivity Process Instance to the Activity that will Error step. Refresh the Instances screen to observe the new Status for this process instance.
- CHECK the box for the GoToActivity Folio Process Instance to select it. Click on the GoTo Activity button, then select the Activity that will Error step. Click OK, then OK again when you see the confirmation message.
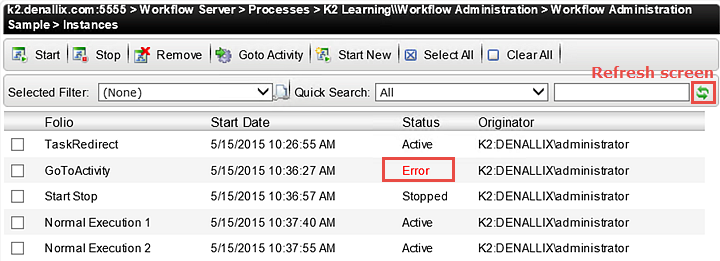
- Refresh the Instances screen by clicking the green icon located on the far right of the navigation bar. (If you use your the refresh button on your browser, you will be redirected back to the K2 Workspace landing page. If that happens, simply navigate back to the Instances screen.)
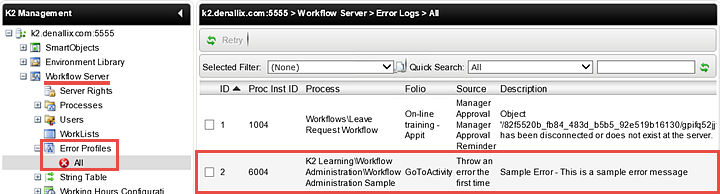
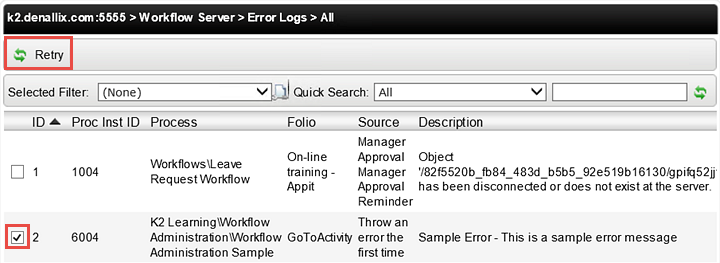
Notice the Status is now showing Error. (We deliberately sent this process instance to a step that would throw an error so that you can see how to repair a failed workflow). The Instances screen is one area in K2 Workspace that indicates if a process instance is in an error state. You can also view process instances that are in an error state by accessing the Error Profiles option located under the Workflow Server node. - In the left column, still under the Workflow Server node, click the Error Profiles option, then All. (It may be easier to collapse the Processes node first.) In this screen, you can view all of the process instances (for all processes) that are in an error state. This screen will also give you a brief description to work from as you begin to troubleshoot.
STEP 3 REVIEW
In this step, we used the GoTo Activity option to redirect a process instance to a different step in the workflow. You will find this tool very useful for sending workflows back to originators or any other user that need to make a change or addition to their form input. We purposely sent this process instance to a step that would throw an error to demonstrate how the Status column updates with a red Error marker. The Instances screen is one area in K2 Workspace that indicates if a process instance is in an error state. You can also view all process instances that are in an Error state by accessing the Error Profiles screen. Here you will also find a brief description of the error to help you as you troubleshoot the issue.
Still on the Error Profiles (All) screen, we will now Retry the instance to see if we can repair it. For this tutorial, we have specifically coded the step to repair itself the second time it is run. A real-world example however, might be if a task was assigned to a new employee, who did not have an email account set up yet. The error might read something like 'destination user not found'. In this case, you could confirm the email account is now set up, then retry the step. K2 would 'see' the user and move the workflow along.
Step 4 Tasks
- Retry the K2 Learning\Workflow Administration\Workflow Administration Sample > GoToActivity Process Instance.
- Access the Process Overview report and confirm the GoToActivity process has completed.
- CHECK the box to the left of the K2 Learning\Workflow Administration\Workflow Administration Sample Process > GoToActivity Process Instance, then click the Retry button.
- Click the Home button to return to the K2 Workspace landing page. Click the Process Overview Report link found in the Reports pane. (It may take a minute to open depending on your environment.)
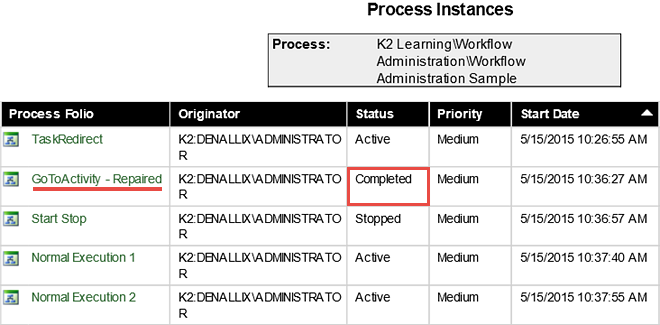
- Click the Workflow Administration Sample Process to access the process instance details. Confirm the GoToActivity Process Instance has Completed.
Now we want to confirm the Process has completed. We will do that by returning to the Process Overview Report and looking at the Process Instance details for this workflow.

STEP 4 REVIEW
In this step, we repaired a process instance that was in an Error state by using the Retry option found in the Error Profiles pane. You can also define additional error profiles to filter errors based on the workflow or the error type. Retrying the error will execute the same event where the error occurred. Use caution when retrying events as you may have unexpected, and possibly duplicate, results based on what the event was designed to do.
Continue on to the next section, Managing Worklists, when you are ready.