Merge syntax
Merge syntax is a templating system based on mustache.js and is used primarily by writing merge variables. These variables are bits of data represented by a parameter wrapped in two or three curly brackets.
For example:
{{someVariable}}
These parameters are then "merged" into another location such as in a UI-only formula, within a component or other component elements.
To automatically insert merge syntax using variables, see Variables.
Merge variables
Merge variables often rely on context to retrieve the variable specified within the curly brackets. Context is determined by where the merge variable is used, and it can be a model record, fields within a record, or a JavaScript object (with or without properties).
Among other things, merge variables are helpful for pulling live data into a location to display to users at runtime. Imagine a builder wants to have a detail panel on the page of an account that displays the name of the account's point-of-contact. To accomplish this, they could use merge variables to fetch the name of the contact from the account record:
First Name: {{firstName}}
Last Name: {{lastName}}
When the detail panel loads in runtime, the merge variables tell Nintex Apps to check the current context—the selected record—to find the values that correspond with the "First Name" and "Last Name" parameters. When Nintex Apps finds that the account record has values for the parameters requested, it passes (or "merges") those values into the location where they were called. So, if the account's point-of-contact was Amy Meerdink, the detail panel displays:
First Name: Amy
Last Name: Meerdink
There are also global merge variables which are available in any merge context, and all start with $ . For example,
{{$Param.accountId}}, {{$Api.Session_Id}}
Builders can access related fields using dot notation within their merge variables. For example, to access related fields off of a related Account record:
{{Account.Name}} ({{Account.City}}, {{Account.State}})
This expression looks to a related object via a reference field called ( Account ). The . then tells Nintex Apps to go within the related object for the Name value.
Other examples of using dot notation include accessing child relationship data, paths to contents within REST models, or accessing global merge variables.
Merge variable formatting
Merge variables can be wrapped in double and triple curly brackets. The number of curly brackets around a merge variable tells Nintex Apps how to format the data represented in the variable when it pulls the data into the targeted location.
{{Amount}}
In most cases, double curly brackets tell Nintex Apps to apply formatting to the data returned to a variable based on the context model's field display type and the running user's locale. For example, say a builder includes the merge variable {{Amount}} , which looks to a currency field on the model called "Amount" that has a value of 3000 .
Because of the double curly brackets, Nintex Apps will check the field's display type ( Currency ) and the user's locale ( en_US ), then apply formatting inherited from those properties to return $3,000.00 .
If the Amount field had a field display type of Number, the result would be 3,000 .
Additionally, double brackets also allow characters that have special meaning in HTML ( & , < and > ) to appear as expected. Double brackets tell Nintex Apps to apply additional HTML to the returned values so that they will display as text instead of being parsed as an HTML directive.
{{{Amount}}}
Triple curly brackets tell Nintex Apps to display only the raw (unformatted) data. Therefore, using the sample value of 3000 , {{{Amount}}} displays as 3000 , regardless of how the field in the original object was formatted.
Merge expressions
Merge variables can be used in a merge expression, which is a string of characters containing one or more merge variables that return a set of values. Merge expressions can be used in some component properties, action properties, UI-only fields, and in JavaScript snippets.
For example:
Full Name: {{First Name}} {{Last Name}}
Address:
{{Street}}
{{City}}, {{State}} {{PostalCode}}
{{Country}}
In runtime, these expressions return:
Full Name: Amy Meerdink
Address:
123 Cephalopod Street
Maritime, Kentucky, 33333
United States
Merge expressions can also incorporate logic, as Nintex Apps's implementation is based on mustacheJS sections. Builders can include limited conditional rendering logic, as well as iterate over arrays.
Merge expression logic will always begin with a pound sign and end with a slash. For example, {{#name}} and {{/name}} .
Conditional merge expressions
The # hash and ^ caret symbols are used to denote truthy or falsy merge expressions, respectively.
For example, to create a conditional merge expression that renders if a field named IsActive is true , you would use the following syntax:
{{#IsActive}}Product is active!{{/IsActive}}
The # tells Nintex Apps if the IsActive field returns true, render "Product is active!"
Conversely, using a ^ will render the content only if the value returned by the IsActive merge variable is false.
{{^IsActive}}Product is not active!{{/IsActive}}
This means that if the returned value of IsActive is false, 0, null, undefined, NaN, an empty string or an empty list, then "Product is not active!" is rendered.
You can use these true or false tags in combination to display a message based on whether a value is true or not. For example:
{{#IsActive}}Sell this product!{{/IsActive}}{{^IsActive}}Pretend this product doesn't exist!{{/IsActive}}
Another example of using the true and false syntax is displaying the quantity of a particular product—but only if the quantity was non-null and greater than 0; otherwise display a link to an Order Form:
{{#Quantity__c}}{{Quantity__c}}{{/Quantity__c}}{{^Quantity__c}}(<a href="/apex/orderForm?code={{{ProductCode}}}">Order Form</a>){{/Quantity__c}}
Looping over arrays
If the target variable of a conditional merge expression is an array (a list of items), then the content of the expression is rendered once for each element in the array. This is commonly used to iterate over records themselves or child relationship records.
To make a merge expression that iterates over opportunity records to display the name, stage, and close date, write something like this:
{{#$Model.Opportunities.data}}
{{Name}} (Stage: {{StageName}}, Close: {{CloseDate}})
{{/$Model.Opportunities.data}}
Or another example, iterating over an account model's data:
{{#$Model.Account.data}}
{{Name}} ({{BillingCity}}, {{BillingState}})
{{/$Model.Account.data}}
For some connections, like Salesforce, it's possible to iterate over child relationship records, if that relationship is available on the model. Nintex Apps stores child records in a special property of the field named records.
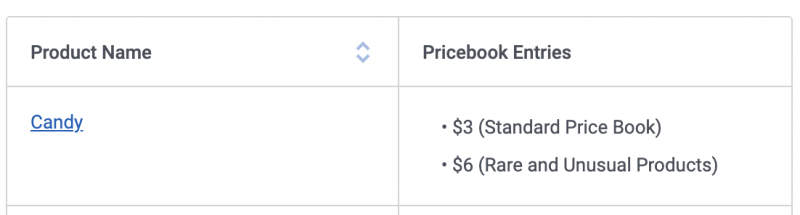
This example iterates over a product's price book entry records to generate HTML list elements:
{{#PricebookEntries.records}}
• {{UnitPrice}} ({{Pricebook2.Name}})
{{/PricebookEntries.records}}
Notice that within the section, merge variables are relative to the current record. So, rather than {{PricebookEntries.records.UnitPrice}} , we use simply {{UnitPrice}} . Pricebook2.Name does use dot notation since it is a reference field on the child relationship.
Note: It's important to add any fields used in a child relationship merge expression to the model through the Child Relationships tab, otherwise your merge expression may appear empty at runtime.
Merge functions
Merge functions are Nintex Apps -defined functions that can be called in any context using expression logic.
For more information, see our global merge variables and functions index.
Using merge expressions in JavaScript
To use merge expressions in JavaScript, call the skuid.utils.merge() API.
For example:
var model = skuid.model.getModel( 'User' ),
row = model.getFirstRow();
var addressExpression =
'{{Street}}\\n' +
'{{City}}, {{State}} {{PostalCode}}\\n' +
'{{Country}}';
element.html(
skuid.utils.merge( 'row', addressExpression, null, model, row )
);
Nintex Apps's merge variable syntax is built on mustacheJS. To use the mustache API directly (to access pre-parsing, for example), access the API via skuid.Mustache. Note that you will not be able to use some of Nintex Apps expression features, such as merge variables.
Troubleshooting
If using sections to help determine a Connection URL parameter for a REST model, you may experience unexpected behavior. Try renaming the field or adjusting the merge syntax.
Check if you are using triple curly brackets instead of double. If the content of the field contains special HTML characters, ( & , < , and > , for example), and you are using triple curly brackets, you may end up with unexpected results. If using triple brackets, try double brackets, and vice versa.
When including a merge variable within an HTML attribute using double curly brackets, your merge variable may return unexpected results. This is due to how Nintex Apps formats the results of merges with double curly brackets; Nintex Apps may be inserting additional HTML into the expression value, which might be causing conflicts with the intended HTML in the expression.
If using double curly brackets, try using triple-curly brackets, which tells Nintex Apps to render the raw value without applying additional HTML.
For more information on double and triple curly brackets, see Merge Variable Formatting
Note: When using triple curly brackets, keep in mind that, if the content of the field contains special HTML characters (for example,``&``, < , and > ), you may end up with unexpected (and very messy) results.