Azure Active Directory
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) is Microsoft’s multi-tenant cloud based directory and identity management service. The Azure Active Directory Service Type provides the ability to read from and manage users and groups in Azure Active Directory. K2 uses this service type for user identification, authorization and integration with Azure AD using the Azure Active Directory workflow wizards.
The Azure Active Directory Service Type exposes Azure AD User methods (such as reading user information, updating user information) Group methods (such as retrieving groups and a user's group memberships) and User-Group operations (such as adding users to groups).
Service Authentication
OAuth is the only supported Authentication Mode for the Azure Active Directory Service Type .
Service Keys (Service Instance Configuration Settings)
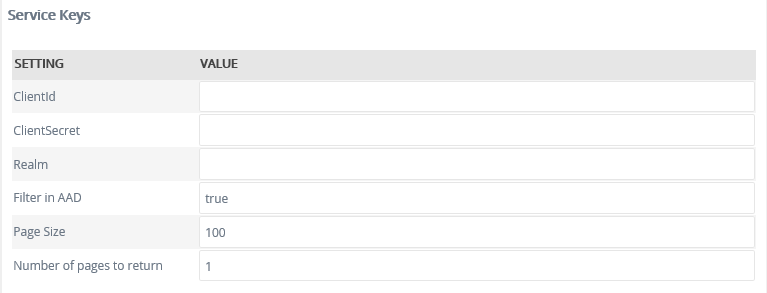
| Key | Can be modified | Data Type | Sample Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ClientId | Yes | Text | 5701318dfgkj654h74332 |
The Client ID from your Azure Active Directory configuration for the App. Normally, this setting is not required unless you have manually configured an application for access in the Azure AD using the Azure Management tools. For more general information see the MSDN article on AAD and OAuth. This property contains sensitive information. You can enter and see your values when you first configure this value. The value will be masked when the service instance is updated. |
| ClientSecret | Yes | Text | fjds543kjdfs87fih234khs |
The Client Secret ID from your Azure Active Directory configuration. Normally, this setting is not required unless you have manually configured an application for access in your Azure AD using the Azure Management tools. (For more information on this, please see this article: AAD and OAuth.) This property contains sensitive information. You can enter and see your values when you first configure this value. The value will be masked when the service instance is updated. |
| Realm | Yes | Text | https://yourtenantname .onmicrosoft.com/yourapp | The APP ID URI from your Azure Active Directory configuration. Normally, this setting is not required unless you have manually configured an application for access in your Azure AD using the Azure Management tools. |
| Filter in AAD | Yes | True/False | True | Filter in AAD sends the filter through to Azure AD to filter before it returns the results. There are limitations regarding filtering in Azure AD, see the Limitations section below. With the setting set to false, the unfiltered results are fetched from Azure AD, and then filtered in the broker. |
| Number of pages to return | Yes | Text | 100 | Azure AD works on a paged request system, so No of pages to return and Page Size are used to manage the number of results to return. This is an important setting when working with the cloud. We recommend 100, as this is also the default Azure AD uses. Increasing the results per page, will require less calls to Azure AD, but will transmit more data over the network at a time, increasing the likelihood of a timeout or disconnect. Decreasing the value can have a performance impact, as more calls are made to Azure AD, and can cause throttling if to many calls are made to a system. Setting this to 0, will bring back all pages, thus return all results, and can have a negative performance impact. But setting to 0 is needed if the FilterInAAD setting is false, as the SmartObject Broker will need all the results, to accurately apply the filter and return the expected results. |
| Page Size | Yes | Text | 1 | Azure AD works on a paged request system, so No of pages to return and Page Size are used together to manage the number of results to return. |
Permissions
The K2 for SharePoint application requires Write permissions, configured in Azure Active Directory, in order for the Create and Update methods to function correctly when using the Azure Active Directory wizards in a workflow.
Service Objects
The Active Directory Service 2 typically exposes the following Service Objects:
- Group (exposes Azure AD Group data and methods))
- User (exposes User level data and methods)
- User and Groups (interacts with the global Azure AD API)
SmartObjects
If an Azure Active Directory environment is configured during installation, K2 automatically generates SmartObjects for these Service Objects. SmartObjects can be automatically created by selecting the Generate SmartObjects for this Service Instance check box when creating a new Service Instance. Designers can use the SmartObject design tools to build advanced SmartObjects that leverage the Service Objects in this service. It is recommended to use the SmartObject design tools to create SmartObjects rather than generating SmartObjects, since this allows better control over the naming, behavior and design of the SmartObject and its methods and properties.
Considerations
The default Service Instance of this service is used internally by the K2 environment. Do not modify or delete the existing service instance. You can create a new instance or use the methods from the existing instance
When applying filters to the Azure AD SmartObject, limitations regarding the Azure AD Service cause different expected behavior. For example, the logical filter “Startswith” is used by the Azure AD Service instead of the “Contains” filter.
Logical filtering that is available in the Azure AD Service:
- Equals
- Startswith
- GreaterThan
- LessThan
Logical filter limitations:
- The “Contains” filter is not available in the Azure AD Service, and when the Azure AD SmartObject applies the “Contains” filter such as used by the Picker control, the “Startswith” filter is applied by the Azure AD Service.
- The “Endswith” filter is not available in the Azure AD Service.
Other limitations
- Only filter on string values (AccountDisable which is bool or OtherMail which is a collection filters will be ignored).
- Some text properties are not filterable at all:
- FacsimileTelephoneNumber
- Mobile
- PhysicalDeliveryOfficeName
- PostalCode
- PreferredLanguage
- StreetAddress
- TelephoneNumber
Azure AD will throw a Microsoft.Azure.ActiveDirectory.GraphClient.UnsupportedQueryException exception and the folowing message will be displayed:
"Unsupported AAD filter used. Revise Filter or disable 'Filter in AAD': Unsupported or invalid query filter clause specified for property 'mobile' of resource 'User'."
This mean the filter contains a field that is not filterable. In this instance the field is called 'mobile'.
SmartForms QuickFilter will filter on all fields, and will cause Azure AD to throw errors if FilterInAAD is enabled.
- These properties are filterable:
- City
- Country
- Department
- DisplayName
- GivenName
- JobTitle
- MailNickname
- ObjectID*
- State
- Surname
- UsageLocation
- UserPrincipalName
*ObjectId cannot be used with other properties in a filter. It must be filtered on its own, else Azure AD will error as above.
- Complex grouping in filters also have a limitation in Azure AD. Azure AD will throw an exception if filter grouping is to complex and will show the following error:
"Unsupported AAD filter used. Revise Filter or disable 'Filter in AAD': Search filter expression has excessive height."
- Filters are not applied when specifying a SmartObject input property. If an input property is specified, the input property is used as an “Equals” logical operation for that field with ‘and’ joins between the properties if multiple expressions are specified, and ignores any filter specified.
- Azure AD only supports filtering a property against a value. So we allow Property=value or Value=Property expressions, but not Value=Value or Property=Property. For example “DisplayName Contains Bob”
- Paging and ordering is not implemented in the Azure AD SmartObject and is handled by the SmartObject Broker on the returned results.
- By default, we set the page size to 100 and to only return 1 page's results.
- FilterInAAD is only implemented for the GetList method on the User and Group Azure AD SmartObject.