Functions
Functions are building blocks that you use to create results using operations and expressions. A function returns the result of operations performed on input values. An expression is built by combining operators and values that evaluate during a workflow. Function objects are displayed in gray.
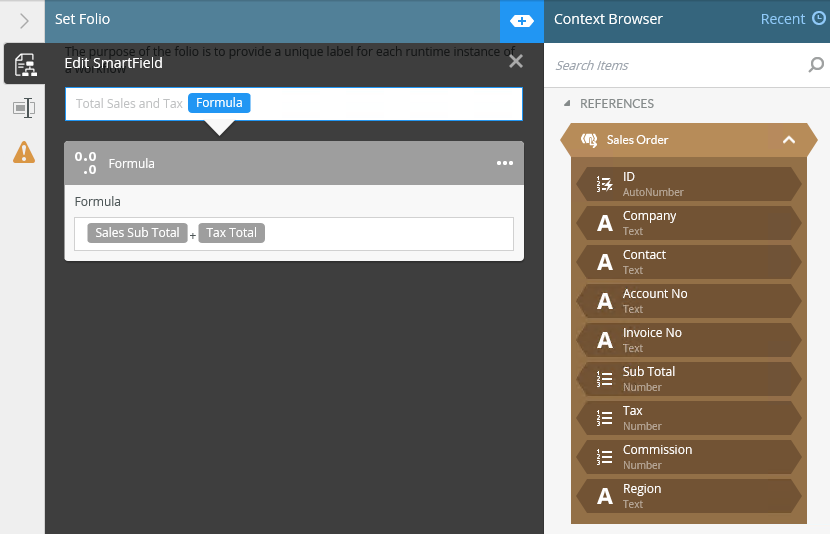
Functions allow you to build simple to complex expressions in any field when designing a workflow. The expressions allow you to calculate dates, concatenate text, do logical and regular expressions, perform math calculations, and perform some file operations. These functions and expressions can be used in rules and as a method to change data coming from another system. Functions are used to both evaluate a condition (true/false) and to return a result, which can be of any type that the K2 platform offers.
The Functions are located within the Context Browser > Function tab.
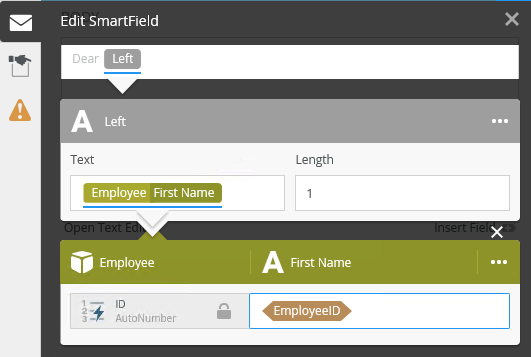
For example, you can use the Smartfield Composer to reduce an employee's first name to the first letter for use as their initial in an email greeting, using the Left text function.
For more information on how to use the All items as a collection option when configuring SmartObjects within the Smartfield Composer, see the How to: Use the All items as a collection option topic.
The success of a conversion depends on the data itself and not only on the input type. For example, converting a long data type to a short works as long as the data itself is convertible, i.e. the number of bits is 16 or less. Converting a decimal to Boolean works as long as the decimal number is 1.0 or 0.0.
Boolean can be converted from a number, where 1 is true and 0 is false. The following table shows the possible accepted input types:
| Function | Accepted input types |
|---|---|
| To Binary | String (Base-64) |
| To Boolean | String, Byte, Short, Integer, Long, Double, Decimal, Boolean |
| To Bytes | String |
| To DateTime | String |
| To Decimal | String, Byte, Short, Integer, Long, Double, Decimal, Boolean |
| To Double | String, Byte, Short, Integer, Long, Double, Decimal, Boolean |
| To Integer | String, Byte, Short, Integer, Long, Double, Decimal, Boolean |
| To Long | String, Byte, Short, Integer, Long, Double, Decimal, Boolean |
| To Short | String, Byte, Short, Integer, Long, Double, Decimal, Boolean |
| To String | String, Byte, List of Byte, Short, Integer, Long, Double, Decimal, Boolean |
| To K2 FQN User | String, String[] |
| To SharePoint Claims User | String, String[] |
Functions
Each function is described in the sections below.
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|

|
Converts an array of bytes to a base-64 encoded string. | Input Value: { 69, 120, 97, 109, 112, 108, 101 } Result: "RXhhbXBsZQ==" |

|
Converts a base-64 encoded string to an array of bytes. |
Input Value: "RXhhbXBsZQ==" Result: { 69, 120, 97, 109, 112, 108, 101 } |

|
Converts a value to a Boolean data type. |
Input Value: "1" Result: True |

|
Converts a string to an array of bytes using the default character encoding. |
Input Value: "Example" Result: { 69, 120, 97, 109, 112, 108, 101 } |

|
Converts a value to a Date data type. | InputValue: "2017/02/02" Result: 2017/02/02 |
|
Converts a value to a DateTime data type. | InputValue: "2017/02/02 05:05:05 AM" Result: 2017/02/02 05:05:05 AM |

|
Converts a value to a Decimal Data type. | Input Value: "1" Result: 1.0 |

|
Converts a value to a Double data type. | Input Value: "1" Result: 1.0 |

|
Converts a value to an Integer data type. | Input Value: "1.0" Result: 1 |
|
Converts an encoded SharePoint claims user or group to K2 FQN user or group. |
Example 1:
Example 2:
Result: K2LDAP:joe;K2LDAP:holly |

|
Converts an encoded SharePoint claims user or group to K2 FQN user or group. |
Example 1:
Example 2:
Result: K2LDAP:joe;K2LDAP:holly |

|
Converts a value to a Long data type. | Input Value: "1.0" Result: 1 |

|
Converts a K2 FQN user or group to an encoded SharePoint claims user or group. | Example 1:
Input Value: c:0-.f|ldaproleprovider|legal Result: K2LDAP:legal Example 2: Input Value: c:0-.f|ldaproleprovider|legal;i:0#. f|ldapmembershipprovider|holly Result: K2LDAP:joe;K2LDAP:holly |

|
Converts a K2 FQN user or group to an encoded SharePoint claims user or group. | Example 1:
Input Value: c:0-.f|ldaproleprovider|legal Result: K2LDAP:legal Example 2: Input Value: c:0-.f|ldaproleprovider|legal;i:0#. f|ldapmembershipprovider|holly Result: K2LDAP:joe;K2LDAP:holly |

|
Converts a value to a Short data type. | Input Value: "1.0" Result: 1 |

|
Converts a value to a String data type. |
Input Value: 12345 Result: "12345" Example 2: Input Value: { 69, 120, 97, 109, 112, 108, 101 } Result: "Example" |

|
Converts a value to a Time data type. | InputValue: "05:05:05 AM" Result:05:05:05 AM |
Date and Time functions perform operations on date and time input values and return strings, numbers, or date and time values.
The following table lists the date and time abbreviations recognized by the Format Date and Time functions.
| Date and Time | Abbreviations | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Year | y, yy, yyyy | 9, 09, 2017 |
| Month | M, MM, MMM, MMMM | 2, 02, Feb, February |
| Day | d, ddd, dddd | 21, Sat, Saturday |
| Hour | h, hh, H, HH | 4, 04, 16, 16 |
| Minute | m, mm | 1, 01 |
| Second | s, ss | 1, 01 |
| Millisecond | ffff | 9999 |
| A.M. or P.M. | t, tt | P, PM |
| Timezone | z, zz, zzz | -6, -06, -06:00 |
The following table lists the standard date and time specifiers recognized by the Format Date and Time functions.
| Specifier | Pattern value (for en-US culture) |
|---|---|
| t | h:mm tt |
| d | M/d/yyyy |
| T | h:mm:ss tt |
| D | dddd, MMMM dd, yyyy |
| f | dddd, MMMM dd, yyyy h:mm tt |
| F | dddd, MMMM dd, yyyy h:mm:ss tt |
| g | M/d/yyyy h:mm tt |
| G | M/d/yyyy h:mm:ss tt |
| m, M | MMMM dd |
| y, Y | MMMM, yyyy |
| r, R | ddd, dd MMM yyyy HH':'mm':'ss 'GMT' (*) |
| s | yyyy'-'MM'-'dd'T'HH':'mm':'ss (*) |
| u | yyyy'-'MM'-'dd HH':'mm':'ss'Z' (*) |
| (*) = culture independent |
The Files inline functions allow you to get information about files, including the content, from various sources.
The return type for all Files inline functions is an XML string. The functions return an XML structure containing the file name and the file contents in Base64, similar to the following:
<files>
<file encoding="Base64">
<name>Leave Policy.docx</name>
<content>JVBERi0xLjSNCiWys7S1...</content>
</file>
</files>
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|

|
Gets a file from data fields, expressions, base64-encoded data and other items containing the file’s content, and allows you to specify a file name. | File Name: The name of the file to return. Content: The contents of the file to return passed any object. For example, input text, a combination of expressions or an object from the context browser. Result: The content of the file as an XML string. |
|
Gets all process attachments. | Workflow Context's Attachment: Attachments are available from Process Instances of workflows that have Attachments enabled . For more information see How to use the Workflow Attachment and Workflow Comment SmartObjects Result: The content of the file as an XML string. |
List functions perform calculations on lists based on input values and returns a number.
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|

|
Returns true if the input values are found. |
|

|
Counts the number of items in a list of values. Values - Input Integer - Return type |
Input Values: { 1, 2, 3 } Result: 3 |

|
Gets the first value in a list. Values - Input Expected When Empty - Object type. This is returned when the input value is invalid Object - Return value |
Values: {1, 2, 3} Expected When Empty: 0 Result: 1 |

|
Gets the last value in a list. Values - Object of array type. e.g. output from a Split() function call can be passed into this parameter. When using an XML node, make sure to use the lowest node in the tree. Index - Number of long type. This specifies the 1-based index of the item in the array. Expected When Empty - Object type. This is returned when the input value is invalid or when the index specified is out of bounds. Object - Return value (Object) is the selected object in the array if there are no errors. |
Example 1: Values: { "a", "b", "c" } Index: 1 Expected When Empty: "empty" Result: "a" Example 2: Values: { "a", "b", "c" } Index: 4 Expected When Empty: "empty" Result: "empty" |

|
Gets the last value in a list. Values - Input Expected When Empty - Object type. This is returned when the input value is invalid Object - Return Value |
Values: {1, 2, 3} Expected When Empty: 0 Result: 3 |
Logical functions performs a logical operation or comparison on objects and expressions, and return a Boolean (True/False) value.
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|

|
Performs an And operation on two Boolean values, returning true if both values are true, false if either value is false. | Input Value: True Input Value: False Result: False |

|
Gets the Boolean value of false. | Result: False |

|
Gets the Boolean value of false. | Result: False |

|
The Not function changes false to true and true to false. Returns a true value if the condition evaluates to false and a false value if the condition evaluates to true. |
Condition: True Result: False |

|
Performs an Or operation on two Boolean values, returning true if one of the values is true, false if both values are false. | Value: True Value: False Result: True |

|
Gets the Boolean value of true. | Result: True |

|
Performs an Exclusive Or operation on two Boolean values, returning true if one and only one of the values is true. | Value: True Value: True Result: False |

|
Gets the Boolean value of true. | Result: True |
Mathematical functions perform calculations, usually based on input values, and returns a number.
| Functions | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|

|
Gets the absolute (positive) value of a number. | Input Value: -1.1 Result: 1.1 |

|
Gets the absolute value of a number. | Input Value: -2 Result: 2 |

|
Calculates the average of a collection of values. | Input Values: { 1.1, 2.2, 3.3 } Result: 2.2 |

|
Formats a number to a text representation using a specified numeric format specified. | Number: 0.111 Format: "C" Result: "$ 0.11" |

|
Use Formula to execute mathematical formulas as a part of rules, mappings, and in notifications. You can only use the following four basic math functions [*, / +, -, and ( )]. You can nest mathematical functions inside another. The exception is you cannot drop a formula function directly into another formula. Tip: When you work with the formula function, always keep in mind the order or operation. PEMDAS (Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication, Division, Addition, Subtraction) or BODMAS ( Brackets, Of or Order, Division, Multiplication, Addition and Subtraction).
|
Input Value: 4*4 Result: 16 |

|
Gets the maximum value of a list of values. | Values: { 1.1, 2.2, 3.3 } Expected When Empty: 0 Result: 3.3 |

|
Gets the maximum value of a list of values. | Values: { 1, 2, 3 } Expected When Empty: 0 Result: 3 |

|
Gets the minimum value of a set of values. | Values: { 1.1, 2.2, 3.3 } Expected When Empty: 0 Result: 1.1 |

|
Gets the minimum value of a set of values. | Values: { 1, 2, 3 } Expected When Empty: 0 Result: 1 |

|
Gets one value raised to the power of another. | Base: 1.1 Power: 1.1 Result: 1.11053424105458 |

|
Gets one value raised to the power of another. | Base: 2 Power: 2 Result: 4 |

|
Gets a random number less than or equal to a specified maximum value. | Maximum: 1.2 Result: 0.5810660167974728 |

|
Gets a random number less than or equal to a specified maximum value. | Maximum: 2 Result: 1 |

|
Gets a random number between two specified values. | Minimum: 0.0 Maximum: 1.2 Result: 0.5810660167974728 |
|
Gets a random number between two specified values. | Minimum: 0 Maximum: 2 Result: 1 |

|
Gets the positive nth root of a positive number. | Number: 32.0 Nth Root: 5.0 Result: 2.0 |

|
Gets the positive nth root of a positive number. | Number: 100 Nth Root: 2 Result: 10 |

|
Rounds a number up or down to a value with a specified precision. | Value: 1.111 Digits: 1 Result: 1.1 |
|
Rounds a value down. | Value: 1.15 Digits: 1 Result: 1.1 |

|
Rounds a value up. | Value: 1.15 Digits: 1 Result: 1.2 |

|
Gets the square of a number. | Number: 2 Result: 4 |

|
Gets the square of a number. | Number: 1.1 Result: 1.21 |

|
Gets the square root of a number. | Number: 1.1 Result: 1.04880884817015 |

|
Gets the square root of a number. | Number: 100 Result: 10 |

|
Gets the sum of a selected value. Use a SmartObject reference with a Get List method to configure the sum value. You can only use one value at a time. To sum multiple values, use the Formula function. For more information on how to configure the Sum function, see the How to: Use the Sum Function topic.
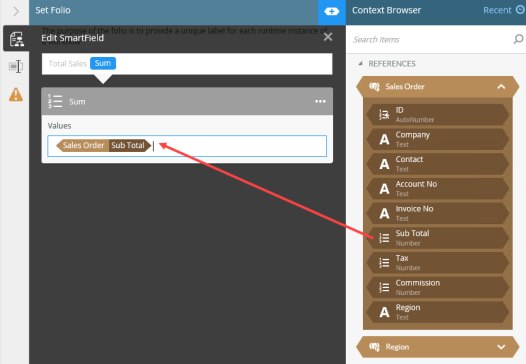 |
Drag the SmartObject reference into the Sum value. |

|
Gets the sum of a selected value. Use a SmartObject reference with a Get List method to configure the sum value. You can only use one value at a time. To sum multiple values, use the Formula function. For more information on how to configure the Sum function, see the How to: Use the Sum Function topic.
 |
Drag the SmartObject reference into the Sum value. |
Regular Expressions provide a powerful, flexible, and efficient method for processing text. A regular expression is a pattern that the regular expression engine attempts to match in input text.
| Functions | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|

|
For doing a regular expression pattern match of a value. e.g. to check if the input value is a valid E-mail address. Input – Input text to search on. This is a string type. Regex Pattern – Regular expression pattern to use for the search. Case Sensitive – Option to indicate whether the search should be case sensitive or not. Return value (Boolean) - is true if a match was found, otherwise false. |
Example 1:
Example 2:
Example 3:
Note that * will always return a match Example 4:
Example 5:
Matches words ending in 'es' Example 6:
Matches words ending in 'es' |

|
To match multiple values from the input string value using a regular expression pattern. e.g. Finding all claim codes in a text form that has “CLM” in front followed by a fixed 5 digit number. Input – Input text to search on. This is a string type. Regex Pattern – Regular expression pattern to use for the search. Case Sensitive – Option to indicate whether the search should be case sensitive or not. Return value (String[]) - is the array of string values that matched the pattern. If there is no match, it returns No match found. |
Example 1:
Example 2:
Example 3:
Example 4:
|

|
To match a single value string from the input string value using a regular expression pattern. e.g. Finding a user’s name specified in a text form. Input – Input text to search on. This is a string type. Regex Pattern – Regular expression pattern to use for the search. Case Sensitive – Option to indicate whether the search should be case sensitive or not. Expected When Empty – String type. This is returned when there is no match found or the matched value is empty. Return value (String) - is the matched string if there is a match. |
Example 1:
Example 2:
Example 3:
Example 4:
Example 5:
|
Text functions perform operations such as concatenations or insertions on text. Text-based operations are 1-based, meaning that the index of the first character in a string is 1.
| Functions | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|

|
Creates a hyperlink with a display name and URL. | Display Name: "K2" URL: "http://www.k2.com" Result: "<a href= http://www.k2.com > K2</a>" |

|
Returns a true value if a substring is found within another string. | Sequence: "12345" Text: "234" Result: True |
|
Returns an empty string. | Result: "Blank" |

|
Returns the index if the specified string is found within another string. Returns 0 if no match can be found. | Substring: "12345" Text: "234" Result: 2 |

|
Inserts a substring into a string at a specified position. | Text: "Example" Substring: "00000" Position: 2 Result: "E00000xample" |

|
Concatenates a list of text values or fields, delimiting each with a separator. | Values: { "1", "2", "3" } Separator: ";" Result: "1;2;3" |

|
Returns a subset of characters from the left side of a string. | Text: "Test" Length: 1 Result: "T" |

|
Returns the length of a string. | Text: "Test" Result: 4 |

|
Returns a subset of characters from a string, starting at a specified index and continuing to the end of the string. | Text: "Example" Start: 3 Result: "ample" |

|
Pads a string with a padding character on the left side up to a specified length. | Source String: "Example" Pad Character: "#" Overall Length: 9 Result: "##Example " |

|
Pads a string with a padding character on the right side up to a specified length. | Source String: "Example" Pad Character: "#" Overall Length: 9 Result: "Example##" |

|
Converts a string to proper case. | Text: "the quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog" Result: "The Quick Brown Fox Jumps Over The Lazy Dog" |

|
Replaces a substring within a string with a new substring. | Text: "Ex000le" Find: "000" Replace: "amp " Result: "Example" |

|
Returns characters from the right side of a string. | Text: "Example" Length: 3 Result: "ple" |

|
Splits text into substrings delimited by a specified separator value. | Text: "a;b;c" Separator: ";" Result: { "a", "b", "c" } |

|
Converts a string to lower case. | Text: "Example" Result: "example" |

|
Converts a string to upper case. | Text: "Example" Result: "EXAMPLE" |

|
Removes leading and trailing spaces and line breaks from a string. | Text: " Example" Result: "Example" |

|
Encodes a URL string. | URL: "http://local.com/test url.asmx" Result: "http%3a%2f%2flocal.com%2ftest+url.asmx" |

|
Decodes a URL string. | URL: "http%3a%2f%2flocal.com%2ftest+url.asmx" Result: "http://local.com/test url.asmx" |