Webservice (SOAP/WSDL)
The Webservice (SOAP/WSDL) service type enables you to call methods from web services by exposing these methods as SmartObjects. The broker utilizes serialization and deserialization to work with complex types, and all method calls are considered stateless
Querying and submitting data using an Endpoint service type can be a complex issue. It requires a good understanding of data and how it is returned from the service call. It also requires understanding the serialization and deserialization methods that are intrinsic to the .NET Framework.
The main methods that are used with the endpoint services are Serialization and Deserialization. Simply put, these methods are used to send and store complex data. To Serialize the results of a service call means to represent it in a state that can be transferred and/or stored, such as in a database. To Deserialize that data is to turn it back into a state that can be consumed. These methods, while based on the .NET Framework for the purposes of the Endpoint service type, represent a device-independent, cross-platform method of representing complex, relational data.
Service authentication
The following authentication modes may be used with the Webservice (SOAP/WSDL) service type:
- Impersonate
- OAuth
- ServiceAccount
- Single Single-on
- Static
Service Keys (Service instance configuration settings)
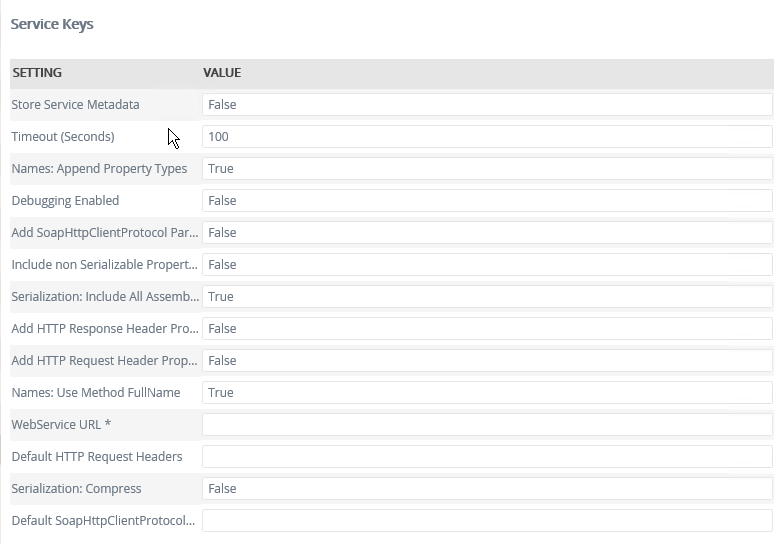
| Key | Can be modified | Data type | Sample value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Store Service Metadata | Yes | True/False | False (Default value: False) |
Sets the ability to store the service metadata of the Web service. Default value: False. If this is set to true service metadata will be stored. |
| Timout (Seconds) | Yes | Number | 120 (Default value: 100) |
Sets the Timout value for the Web Endpoint service. |
| Names: Append Property Types | Yes | True/False | True (Default value: True) |
Includes the property type in parentheses after the complex property name. |
| Debugging Enabled | Yes | True/False | False (Default value: False) |
Displays stack trace information in dialog and error information. |
| Add SoapHttpClientProtocol Parameter To Methods | Yes (required) |
True/False | False (Default value: False) |
Adds a SoapHTTPClientProtocol as a Parameter to Service Object methods. The Parameter values are passed to the target service as HTTP header parameters. See the section below for more information. |
| Include non Serialized Properties | Yes | True/False | False (Default value: False) |
If the value of this Key is set to True it will add non-Serializable properties on the Serialize method Input values. |
| Serialization: Include All Assembly Types | Yes | True/False | True (Default value: True) |
Includes all available serialization objects regardless of usage in public methods. |
| Add HTTP Response Header Property to Methods | Yes | True/False | False (Default value: False) |
Set this property to True if you need to get the HTTP response per method call. |
| Add HTTP Request Header Property to Methods | Yes | True/False | False (Default value: False) |
If you need to use HTTP request headers for the Web service, set this property to True and then add the credentials in the Default HTTP Request Headers property. |
| Names: Use Method FullName | Yes | True/False | True (Default value: True) |
Uses the full name of the method including the property names and types. |
| WebService URL | Yes (required) |
Text | http://localhost/servicemodelsamples/ service.svc?wsdl | The URL to the service description (WSDL) for the Web service. WSDL will automatically be appended if not found in the URL. |
| Default HTTP Request Headers | Yes | Text | Add your credentials into this field when Add HTTP Request Header Property to Methods is set to True. | |
| Serialization: Compress | Yes | True/False | False (Default value: False) |
Compress the serialization data for complex types. |
| Default SoapHttpClientProtocol Value | Yes | Text | The default value for the SoapHTTPClientProtocol value. This value must be created with the Serialization object generated for the service (see the section below for more information). Note that if a value is provided for the SoapHttpClientProtocol at runtime, that value will overwrite the default value |
Service objects
When generating SmartObjects for an Endpoint service instance, some standard categories of SmartObjects are created; for example, the Object Types, and System Types. These define the data types used. Other SmartObjects may be generated depending on what the Endpoint exposes.
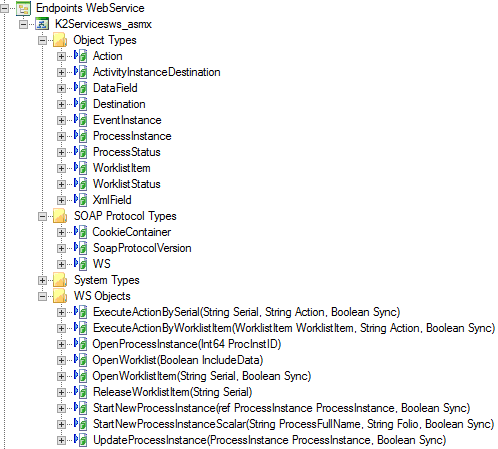
SmartObjects
The product does not automatically create SmartObjects for the service objects in this service. SmartObjects can be automatically created by selecting the Generate SmartObjects for this Service Instance check box when creating a new service instance. Designers can use the SmartObject design tools to build advanced SmartObjects that leverage the service objects in this service. It is recommended to use the SmartObject design tools to create SmartObjects rather than generating SmartObjects, since this allows better control over the naming, behavior and design of the SmartObject and its methods and properties.
Considerations
- When working with EndPoint SmartObjects, an understanding of serialization and deserialization is essential. See Working with EndPoint SmartObjects for more information.
- For troubleshooting tips, please see Troubleshooting the EndPoint service types