Understanding Environment Libraries
Many organizations have multiple environments, for example Development, Test, QA and Production. These environments usually have different server names, URL’s settings and so on. The product makes provision for multiple environments with the Environment Library, which is essentially a repository of environment-specific values or "placeholders" for each of your environments. Consider the table below:
| Environment Field | Environment | |
|---|---|---|
| Development | Production | |
| SharePoint Portal URL | http://devportal.denallix.com | http://portal.denallix.com |
| Email Server | devmail.denallix.com | mail.denallix.com |
When building workflows or SmartForms, designers you may need to interact with different environment fields. Here is an example: Perhaps you want to use a custom environment field in the email step in your workflow.
Create a custom environment field in Management. For the purpose of this example, a new miscellaneous field is created in Management, called Customer Public URL, this field links to URL for customer to access.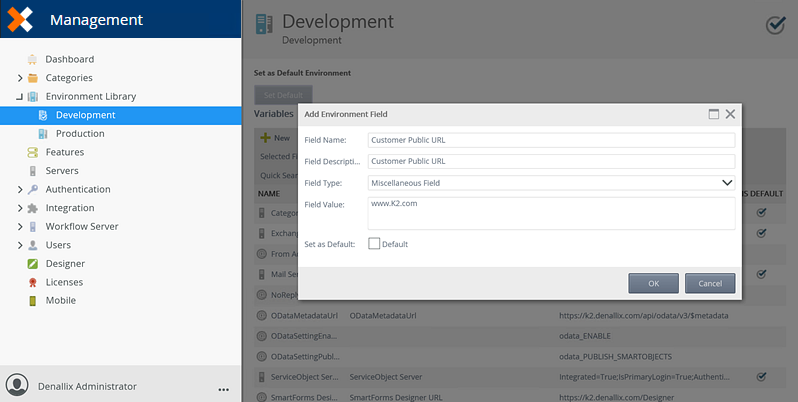
In the Email step of your workflow, expand the Context Browser. Expand the Environment Libraries drop down and drag the custom environment field into the body of Email step.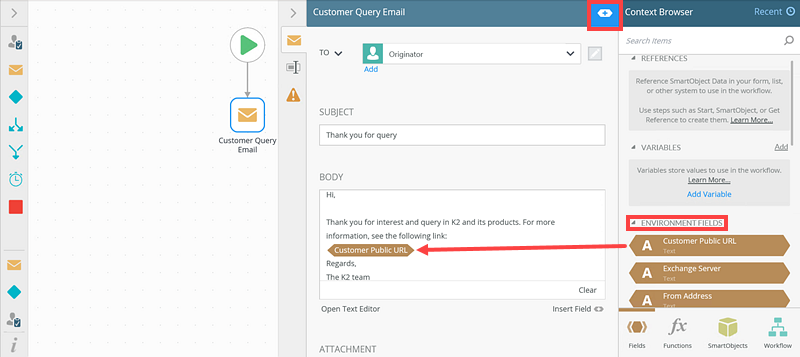
You can also use environment fields in the Designer, see the below: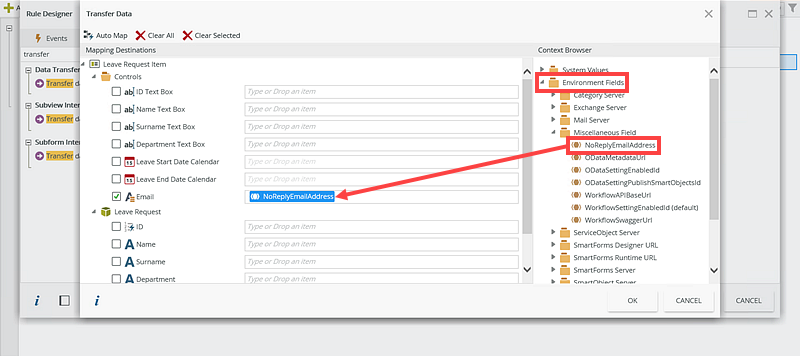
Environment fields are stored on a server, and the product is “context-aware” at runtime. This means that even if one environment contains multiple copies of the same placeholder for each environment, when the workflow retrieves an environment field at runtime, the product will know which values to use for the placeholder for the current environment. The currently-active environment is defined by the "Default" setting for the environment.
The default values in the environment library are set up when upon installation, but it may be necessary to update these values from time to time. This can be done by the administrator using the Management site. The values are centrally stored on the server.
Environment Fields and Package and Deployment
When dealing with environment fields and Package and Deployment, see the Package and Deployment Considerations topic.
Environment Fields and Environment Libraries
See Using environment fields in a workflow and switching between environment libraries for information about using environment fields in different environment libraries.