Configuring the Active Directory User Manager (ADUM)
The Active Directory user manager is the default user manager installed on most systems. If AD is not detected during installation, you have the option to configure SQL as the user manager.
You can have multiple SQL, LDAP, and custom user managers.
All values below are disabled by default, and the default cache timeout is set to 10 minutes.
User Manager Settings
The AD user manager returns all results for the queries passed to it. You can limit the number of users and groups returned for better performance if you have a large directory. Use the User Management page on the Users node of the Management site to limit the number of users returned. The default value is 100 when specifying a limit.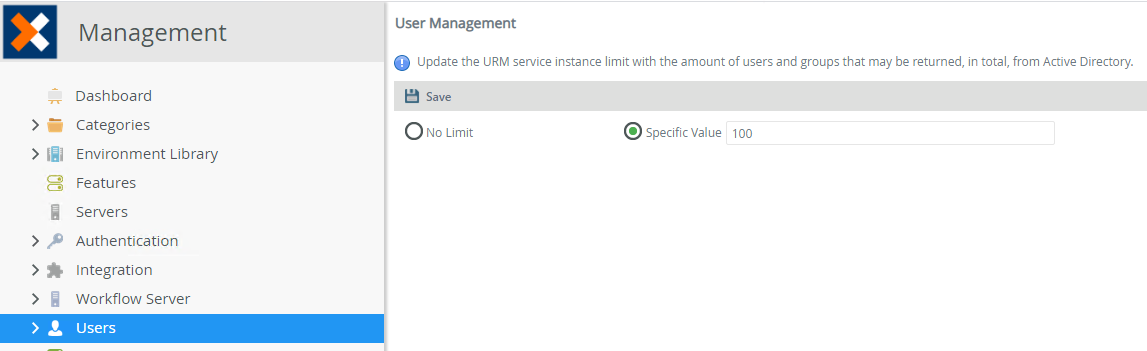
Use the Management site to configure the AD user manager. Browse to the site and expand Users, select the default AD security label node K2 to configure Domain Settings.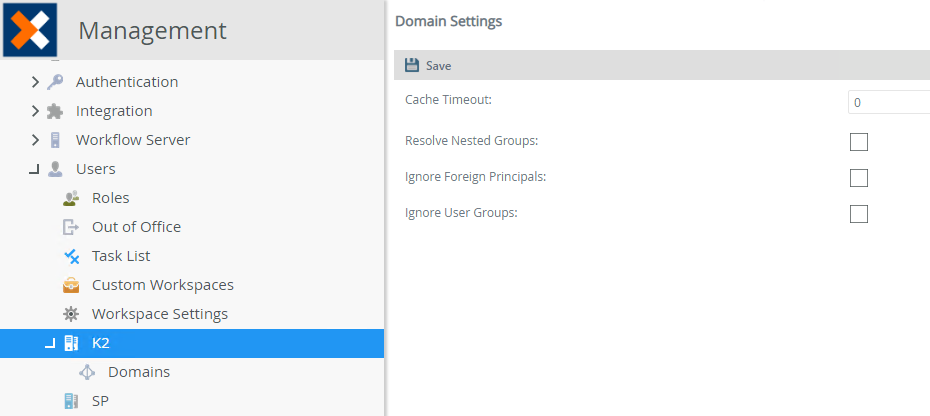
| Settings | Description |
|---|---|
| Cache Timeout | The system caches a user's credentials when used for the first time. The cached credentials get supplied if needed again during the timeout period. If the timeout period has expired, the system will interrogate the AD user manager to return user authentication. Specify the timeout interval in whole minutes only. |
| Resolve Nested Groups | AD groups may contain nested groups within a group. Enabling this option resolves users within these nested groups. |
| Ignore Foreign Principals | This setting either allows (when False) or denies (when True) membership principals from foreign domains from resolving. Also referred to as cross-domain or cross-forest membership, Foreign Security Principals allows users from a different domain ( DOMAIN-B) to become members of groups on another domain (DOMAIN-A). If a group contains a foreign principal, and this setting is False, the product resolves the user. If the setting is set to True, the user or group is not resolved. |
| Ignore User Groups | This option lets the you control whether user groups (Distribution Groups) are resolved.. |