Dynamics CRM
The Dynamics CRM Service Type is used to expose CRM entities in a Microsoft Dynamics CRM Organization as SmartObjects.
You can create an instance of this Service Type for your CRM server and additional instances to target additional CRM Servers or Organizations. The CRM Service Type works in conjunction with the CRM Functions Service Type. Note that the CRM Functions broker does not require an instance per CRM Organization, since it works dynamically across any CRM instance.
Service Authentication
The table below describes the Authentication Modes that may be used with the CRM Service Type.
| CRM On-premises | CRM in the Cloud |
|---|---|
|
|
Service Keys (Service Instance Configuration Settings)
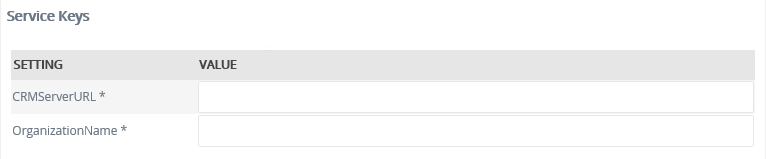
| Key | Can be modified | Data Type | Sample Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRMServerURL | Yes (required) |
Text | https://portal.denallix.com/CRM | Provide the CRM Server's URL |
| OrganizationName | Yes (required) |
Text | denallix | Provide the CRM Organization Name for the organization defined in CRM that will be associated with this Service Instance. See Organization Name in Microsoft Dynamics CRM 2011. |
Service Objects
The Dynamics CRM Service typically exposes multiple Service Objects for the entities discovered when a Service Instance is registered. The list of exposed entities and methods can be seen in the following embedded Excel spreadsheet: CRM_MethodMatrix.xlsx. The CRM Service Broker exposes certain Entities (as described in the Excel sheet) and within each resulting ServiceObject, only certain methods are exposed. Not all Entity fields are created all the time. As per Microsoft's recommended best practice, the CRM API SdkMessageFilter is used to determine which methods to expose.
Each field in an entity has the following properties:
- IsValidForCreate
- IsValidForUpdate
- IsValidForRead
When describing the methods and creating the resulting ServiceObjects, the service broker filters out all fields whose value is false for the above mentioned properties, to avoid runtime exceptions. The SdkMessageFilter is then used to determine which methods it should expose for each entity. This is why certain Entities have all the methods and other Entities have only some of the methods.
The screenshot below shows some typical entities that are exposed when registering an instance of the CRM service, though the entities available in your environment may be different. 
SmartObjects
If a CRM environment is configured during installation, K2 automatically generates SmartObjects for these Service Objects. SmartObjects can be automatically created by selecting the Generate SmartObjects for this Service Instance check box when creating a new Service Instance. Designers can use the SmartObject design tools to build advanced SmartObjects that leverage the Service Objects in this service. It is recommended to use the SmartObject design tools to create SmartObjects rather than generating SmartObjects, since this allows better control over the naming, behavior and design of the SmartObject and its methods and properties.
Considerations
- To use the K2 CRM SmartObjects and workflow wizards with Office 365, CRM must be activated within Office 365.
- The default Service Instance of this service is used internally by the K2 environment. Do not modify or delete the existing service instance. You can create a new instance or use the methods from the existing instance