OData
The OData Service Type enables you to call methods from OData-compliant service endpoints by exposing these methods as SmartObjects.
OData is the protocol that enables the creation and consumption of REST APIs. These APIs allow URL-based resources (defined by a data model) to be accessed and used via HTTP messages. It shares some similarity with JDBC and ODBC, but OData is not limited to relational databases. The following resources contain additional background information on the OData protocol. This topic assumes that you are familiar with OData, so it might be worthwhile to read the links below before attempting to use the broker.
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Open_Data_Protocol
- http://www.odata.org/documentation/odata-version-3-0/odata-version-3-0-core-protocol
The K2 OData endpoint broker is similar to the other endpoint brokers in that it exposes entities, objects and system types based on an OData endpoint.
Service Authentication
The following Authentication Modes may be used with the OData Service Type:
- Impersonate
- OAuth
- ServiceAccount
- Single Single-on
- Static
Service Keys (Service Instance Configuration Settings)
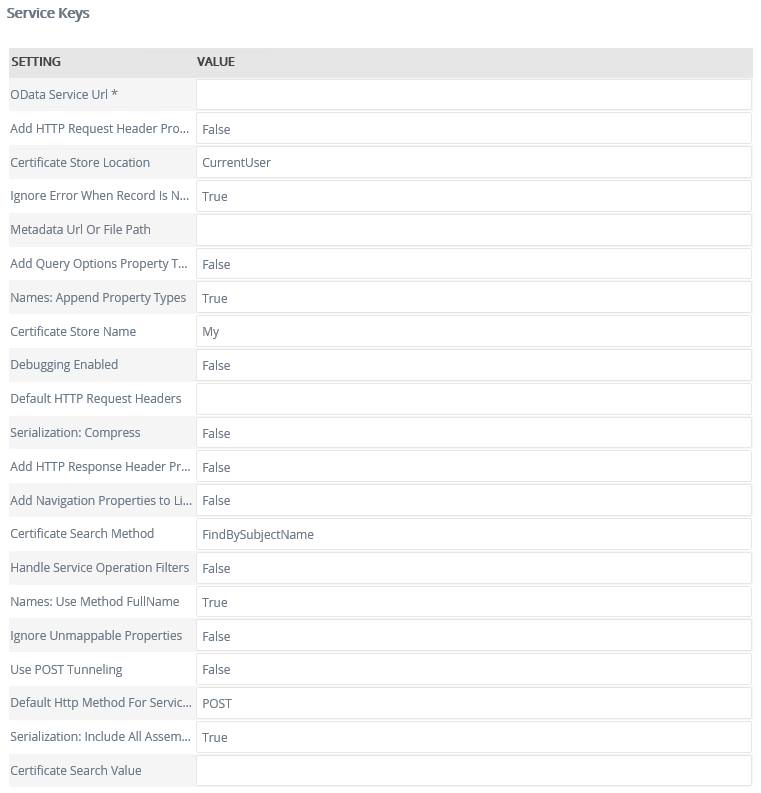
|
Service Key |
Default value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
OData Service Url |
The URL to the OData Service. |
|
|
Serialization: Compress |
False |
Compress the serialization data for complex types. |
|
Serialization: Include All Assembly types |
True |
Includes all available serialization objects regardless of usage in public methods. |
|
Names: Append Property Types |
True |
Includes the property type in parentheses after the complex property name. |
|
Names: Use Method FullName |
True |
Uses the full name of the method including the property names and types. |
|
Debugging Enabled |
False |
Displays stack trace information in dialog and error information. |
|
Add HTTP Request Header Property To Methods |
False |
Adds an optional property to each method to allow for a list of HTTP Request Headers to be sent to the service. |
|
Add HTTP Response Header Property To Methods |
False |
Adds an optional property to each method to allow for a list of HTTP Response headers to be returned from the service. |
|
Ignore Error When Record Is Not Found |
False |
Tells the service broker whether it should throw an error when it fails to find a record. |
|
Ignore Unmappable Properties |
False |
Tells the service broker whether it should throw an error when an entity has unserializable properties on execution. |
|
Use POST Tunneling |
False |
Some OData services only allow GET and POST operations. This value tells the broker whether it is allowed to use other HTTP verbs such as PUT and DELETE. |
|
Default Http Method For Service Operations |
POST |
Tells the service broker whether it should default Service Operation executions to either an HTTP GET or POST. |
|
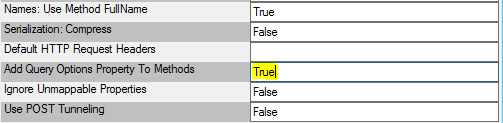
Add Query Options Property To Methods |
False |
This setting adds the Query Options input property to the Entity and Service Operation smart objects. The Query Options field is used to supply advanced query parameters that the SmartObject framework filter does not handle such as $Skip, $Take, etc. |
|
Default Http Request Headers |
null |
This is used to supply default HTTP headers that should be added onto every HTTP request. The non-default value expected can be created using the HttpHeader SmartObject found in the ObjectTypes folder of this service broker. |
|
Handle Service Operation Filters |
False |
Not all OData services allow clients to query the results of Service Operations. When this setting is set to false, filters will be handled in the SmartObject framework. Setting this value to true will cause the filter to be added into the service query. |
|
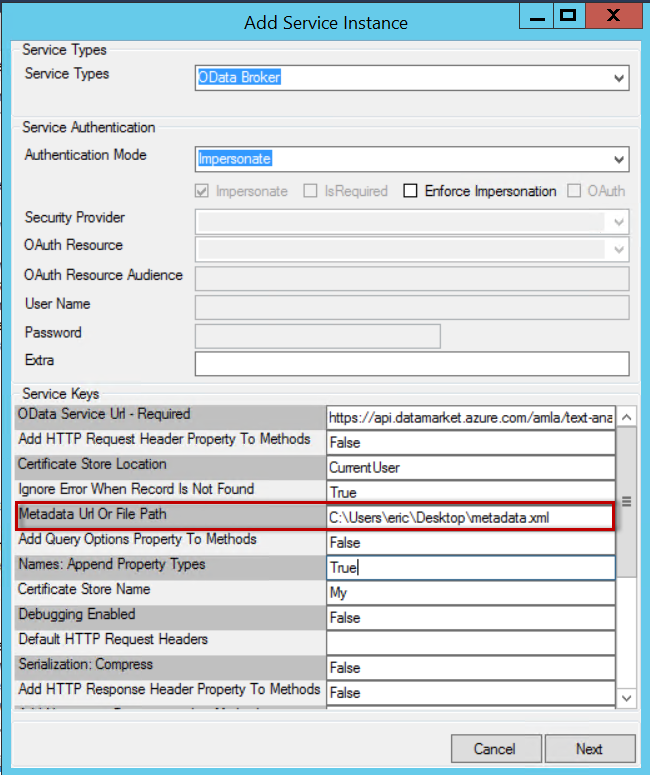
Metadata Url Or File Path |
null |
Some OData services may restrict who has access to its metadata or choose to store its metadata in another location. To accommodate this, this config setting takes an alternative local file path or external url pointing to the service’s metadata. |
|
Add Navigation Properties to List Methods |
false |
This config setting toggles navigation input properties on or off. These navigationproperties show up on the brokers list method’s to allow additional filtering capabilities. |
|
Certificate Store Name |
My |
This config setting is only used when the Certificate Search Value config setting is not set to null. The name of the certificate store under which the client certificate is installed. The valid values for this config setting are: AddressBook, AuthRoot, CertificateAuthority, Disallowed, My, Root, TrustedPeople, and Trusted Publisher. Please refer to: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.security.cryptography.x509certificates.storename.aspx for more information. |
|
Certificate Store Location |
CurrentUser |
This config setting is only used when the Certificate Search Value config setting is not set to null. The location of the certificate store to open. The valid config values are CurrentUser and LocalMachine. Please refer to: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.security.cryptography.x509certificates.storelocation.aspx for more information. |
|
Certificate Search Method |
FindBySubjectName |
This config setting is only used when the Certificate Search Value config setting is not set to null. The method with which to search the opened certificate store for the client certificate. There are a number of search options available including searching by name or thumbprint. Please refer to: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.security.cryptography.x509certificates.x509findtype.aspx for a complete list of all valid config values. |
|
Certificate Search Value |
null |
The search value to use when looking for a client certificate. Filling in this config setting will cause the broker to expect to find a valid certificate at the specified location. An error will be thrown if a valid certificate is not found (this includes the case where a certificate is found, but the certificate is invalid due to expiration or lack of trust). |
Service Objects
The broker will create Service Objects for the entities, objects and system types in the targeted service endpoint. See the sections below for more information on how the Broker creates and manages Service Objects.
The OData service broker supports OData’s Service Operations. (Service Operations should not be confused with Actions and Functions, which are similar in nature. The broker does not expose Actions and Functions). Service Operations appear in the Operations folder. Each Service Operation is represented by a Service Object. A Service Operation Service Object exposes either a Load or an Execute method, or the three list methods (List, List To Serialized Item, and Read To Serialized Item).
Service Operation Service Objects discover all of the input properties, the return type, the function name, and required properties. They also handle all of the query string or body parameter construction.
A Service Operation can be bound to a particular entity or entity set. If a Service Operation is bound to a particular entity, the Service Operation allows you to specify that entity by exposing the primary keys of the entity as input properties.
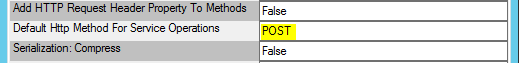
The default HTTP method type for a Service Operation is POST. This default is used when the service does not specify a method type for a Service Operation. To override this default, the Default Http Method For Operations service key setting is provided in the service instance configuration. The two valid values are GET and POST. Any other values will cause the broker to default back to POST.
Service Operations have a naming convention consisting of:
MethodName (dataType + parameter , dataType + parameter)
So a service operation called MyServiceOperation with a text parameter of myString and a number parameter of myNumber would have the service object name:
MyServiceOperation(String myString, Int32 myNumber)
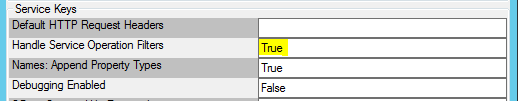
Due to ambiguity issues that can be present in OData implementations, filtering will work, but it will not be executed in the OData service by default. All filtering on service operations is done in the SmartObject framework unless the HandleServiceOperationsFilters config setting is set to True:
The screenshot below is a sample of the Service Object representation of OData.Org’s sample service operations: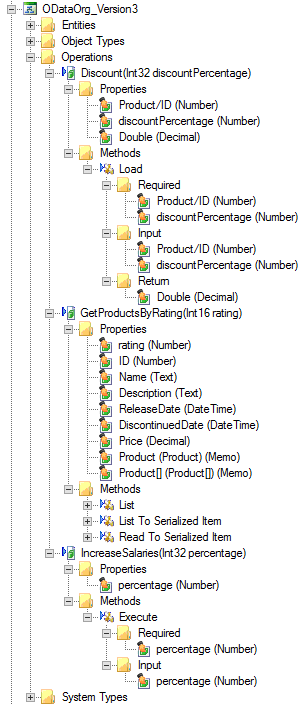
The GetProductsByRating service operation’s List method on the OData.Org sample service:

When a relationships exists between entities, the service broker exposes these relationships on the list methods, if the Add Navigation Properties To List Methods service key setting is True.
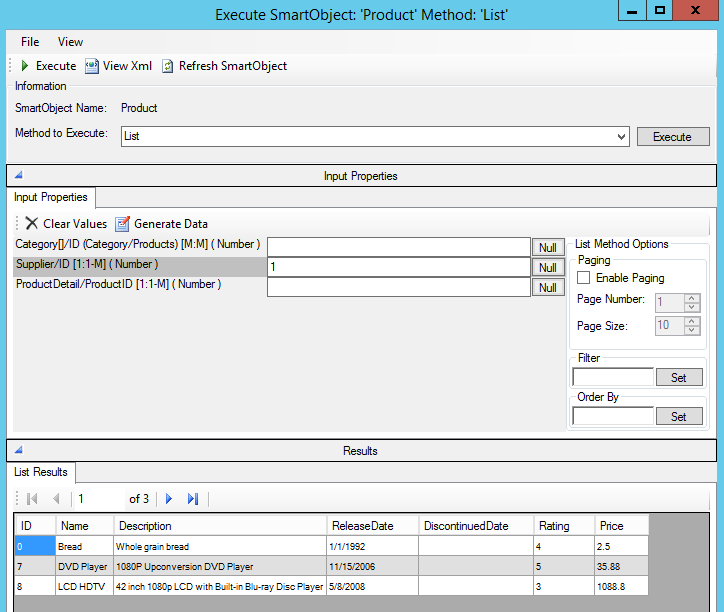
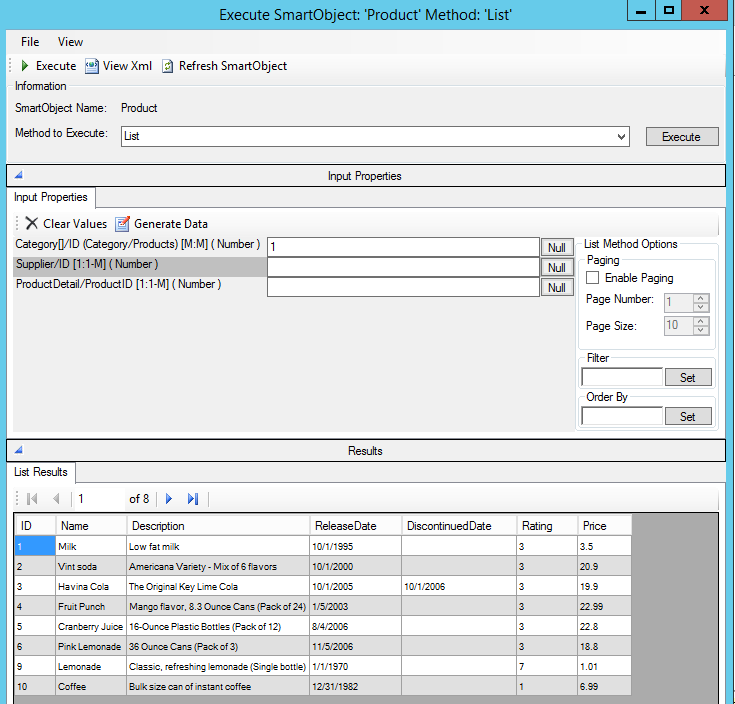
One-One/Many (1:1-M)
In this example, Product has a 1:M relationship to Supplier. Each Product has one Supplier and a Supplier can have many Products. On the List method for the Product you see the Supplier/ID, which allows you to return products from a particular supplier. If you wanted to return all the products from a particular supplier you would pass in the supplier ID:
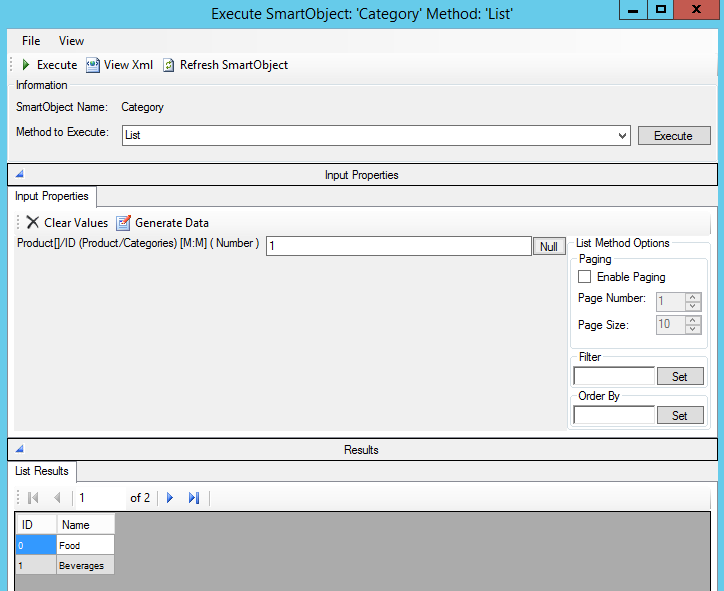
Many-One/Many-Many (M:M or M:1)
A Product has a M:M relationship to Category. Each Product can be in multiple Categories and each Category can have multiple Products.
For example, to get all the categories a product is in, pass in the product ID to the Category List method:
To get all the products in a category, use the Product List method and pass in the Category ID:
The OData broker handles complex SmartObject filtering. The SmartObject filter is translated to the corresponding URL to improve performance. For example, if you wanted to get all the Products where the Name starts with B and the Rating is greater than 1 you would use the following filter:
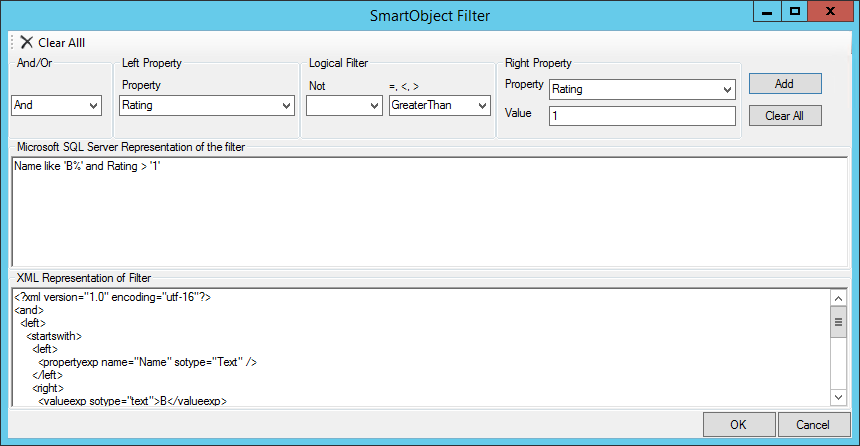
The corresponding URL looks like this: http://services.odata.org/V3/(S(omdt3ebrzqrvcyfv1gsi5noq))/OData/OData.svc/Products()?$expand=Supplier,ProductDetail&$filter=startswith(Name, 'B') eq true and Rating gt 1
If the SmartObject framework filter does not expose the functionality necessary for your query, an additional parameter can be used to create custom queries. To turn this input parameter on, the set the Add Query Options Property To Methods service key to True. Once you to, the parameter appears on the Load, List, ListToSerializedItem, and ReadToSerializedItem methods.
Then custom queries like this one becomes possible:http://services.odata.org/OData/OData.svc/Products?$top=5&$skip=2
This would be constructed in the SmartObject Service Tester like the following example: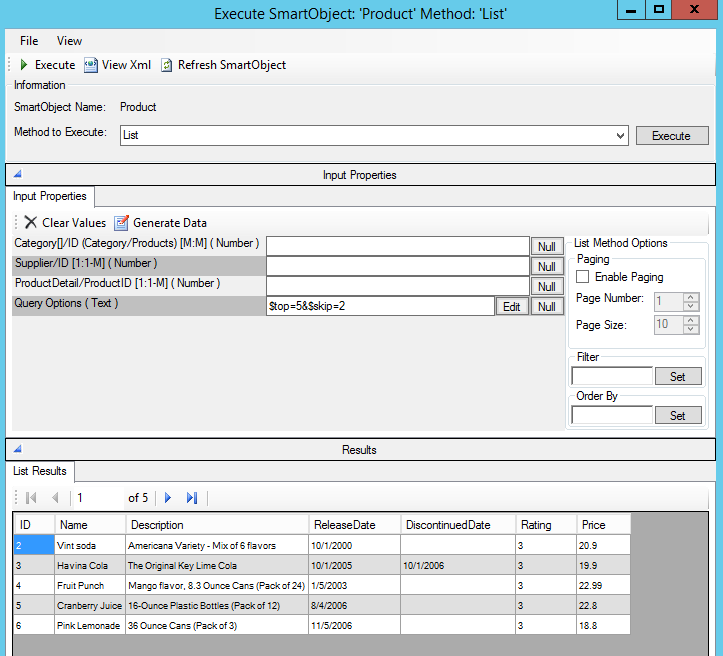
The Query Options input property can be used in conjunction with the SmartObject filter safely. The OData service broker handles combining the two parameter groups together.
The Query Options supported are
- $filter
- $skip
- $top
- $take
- $orderby
- $select
Query options which return values other than those described on the service object method will not work.
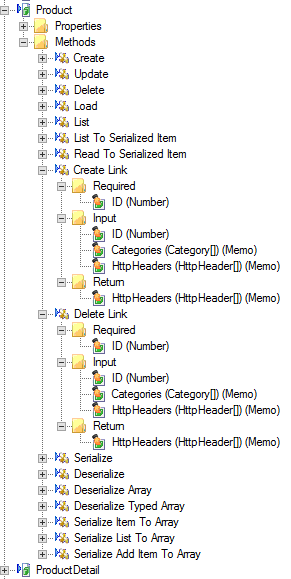
Calling the Create or Delete methods does not create or delete Links to other entities. Instead use the Create Link and Delete Link methods to manage links between entities. These methods only appear on Service Objects in the Entities folder that have either one-to-many or many-to-many relationships with another entity. Many-to-One relationships must be set up through the other side of the relationship.
For example:
A Company has many Employees, but an Employee has only one Company.
Only the ‘Company’ Service Object exposes the Create Link and Delete Link methods.
An example of the Create Link and Delete Link methods on the Product entity from odata.org’s V3 service.
(The Product entity has a many-to-many relationship with the Category entity)
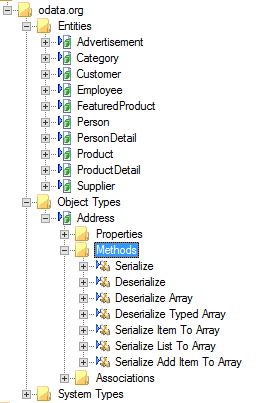
If an entity contains a complex type that is not an entity, then a Service Object is created for the complex type but without the CRUD methods. All complex types in service brokers are handled using serialization and deserialization, For more information please read the Serialization/Deserialization topic.
OData Services have the option to expose files through resource streams. Media resources are exposed through the /$value route on the end of an entity’s URL. The URL to retrieve a media resource from an entity called ‘MediaEntity’ would be: http://myservice.com/OData/OData.svc/MediaEntity(1)/$value.
Named resources are exposed in a similar fashion but specify the property they apply to. The URL to reach the named resource on an entity with a property named ‘Photo’ would be: http://myservice.com/OData/OData.svc/NamedResourceExample(1)/Photo/$value.
If an entity exposes a media or named resource, then it also exposes two methods: Load Without Content and List Without Content. These methods only return the basic properties and the URL pointing to the media or named resource. The standard Load and List methods return URLs and the full media or named resource files.
Example of the Hyperlinks on a media resource stream’s List Without Content method:
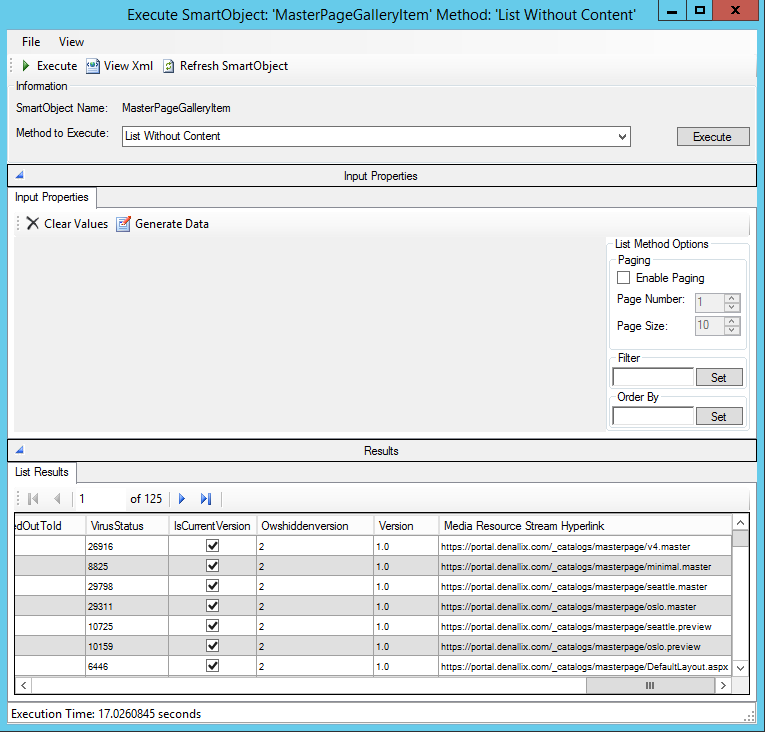
Media and Named Resource Streams are supported in the OData Broker through FileProperties. The FileProperties are only exposed on the basic CRUD methods. List methods do not retrieve resource streams. Instead, list methods expose the hyperlinks to the URLs of the resource streams that can be used in your applications or forms.
Media and Named Resource Streams also expose additional properties to support the main file property. These properties are the Media/Named Resource Stream Path and the Resource Stream MIME Type properties.
The MIME Type property is used to indicate the MIMEType of the file being saved through the ContentType header on the HTTP request to the service. If the MIMEType property is populated, its value overrides the file’s extension and any other internal processing the broker might use to figure out the MIMEType.
The Path property is used to set the Slug header on the HTTP request. If this header is left empty, the Slug header is not added to the HTTP request. The Slug header is often used in OData services to indicate where the resource stream should be saved on the server. There is no processing on the value in this property so if the service requires the Slug header to be populated for reasons other than path specification, this property can be used.
An example of a Media Resource Stream being retrieved: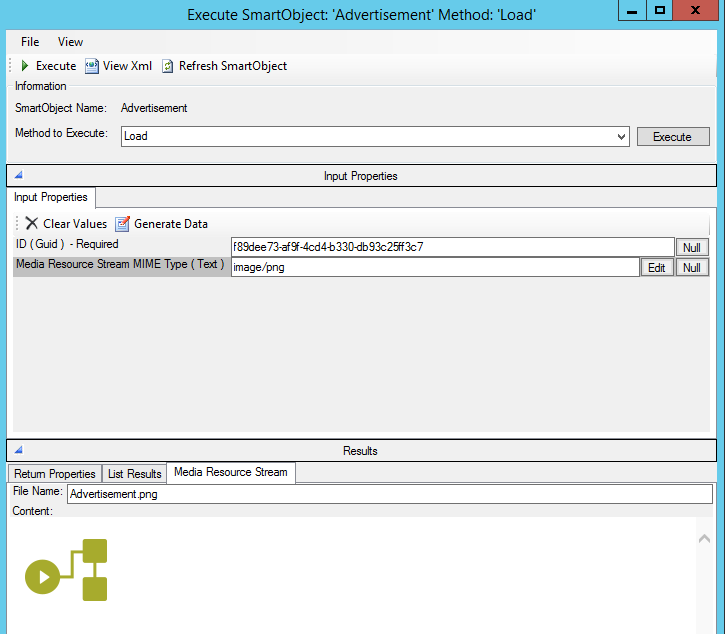
An example of the Media Resource properties on an update method: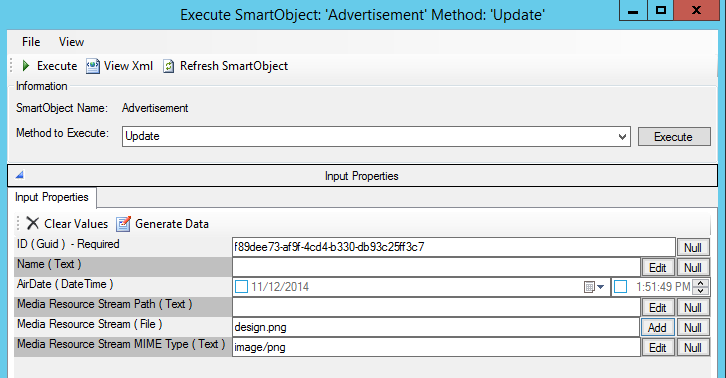
An example of a Named Resource Stream for a Photo property being retrieved: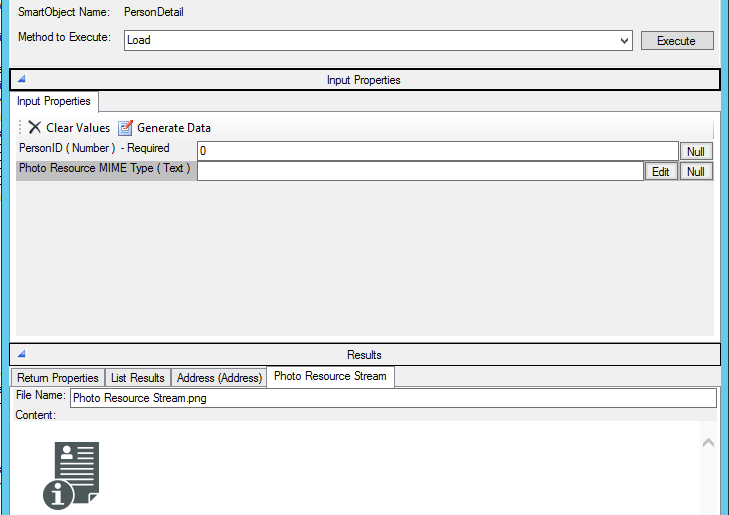
An example of the Named Resource properties for the Photo property on the Create method: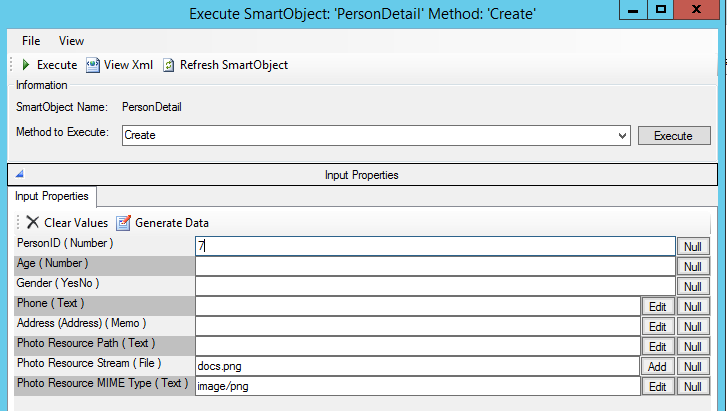
SmartObjects
K2 does not automatically create SmartObjects for the Service Objects in this service. SmartObjects are automatically created when selecting the Generate SmartObjects for this Service Instance check box when creating a new Service Instance. Designers may use the available Service Objects in this service to create advanced SmartObjects using the available K2 SmartObject design tools. It is recommended to use the K2 Design tools to create SmartObjects rather than generating SmartObjects, since this allows better control over the naming, behavior and design of the SmartObject and its methods and properties.
Considerations
- At the time of release, the OData service broker was tested up to Version 3.0 of the OData standard. See the topic Determine if a Service is OData compliant for guidance on testing whether a service is compliant with the OData standard. If you are working with an unfamiliar service or experience trouble when registering an instance of the broker, we recommend that you follow the steps in that topic to determine whether the service is OData compliant.
-
You can use a sample OData service to test the OData service broker. Using a web browser, navigate to
http://services.odata.org/V3/(S(readwrite))/OData/OData.svc/
This will generate a unique “read-write” OData service with a unique URL to test with. Use the URL generated for your test service, and register an Instance of the OData Service using that unique URL. You will see several Service Objects discovered, which you can then generate or create SmartObjects for.
Known Issues
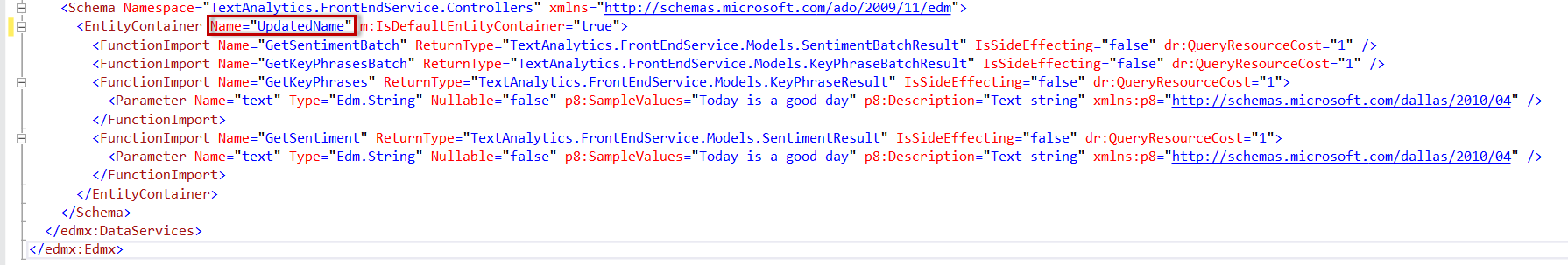
If the EntityContainers name matches part of the service namespace a conflict occurs when registering the service causing an error. An example of the type of error is shown below: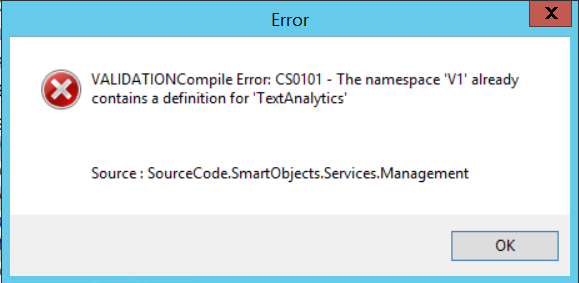
The conflict can be seen in the service metadata XML. In the following example TextAnalytics is the EntityContainer Name and it is also part of the Namespace. TextAnalytics.FrontEndService
There are two ways to resolve the issue:
- Change the system name when registering the service to match the name causing the conflict.
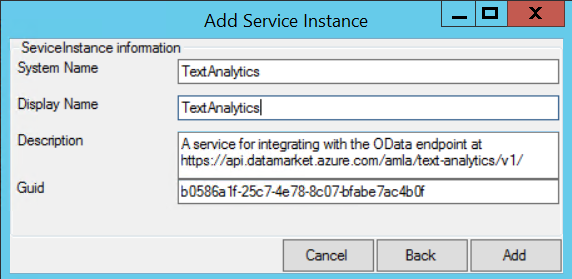
- Download the XML metadata file, edit the EntityContainer Name to any other name, save the file and then change the metadata URL to point to your updated XML file.