Endpoints WCF
The Endpoint WCF Service Type enables you to call methods from Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) endpoints by exposing these methods as SmartObjects. The broker utilizes serialization and deserialization to work with complex .NET types, and all method calls are considered stateless
Querying and submitting data using an Endpoint Service Type can be a complex issue. It requires a good understanding of data and how it is returned from the service call. It also requires understanding the serialization and deserialization methods that are intrinsic to the .NET Framework.
The main methods that are used with the endpoint services are Serialization and Deserialization. Simply put, these methods are used to send and store complex data. To Serialize the results of a service call means to represent it in a state that can be transferred and/or stored, such as in a database. To Deserialize that data is to turn it back into a state that can be consumed. These methods, while based on the .NET Framework for the purposes of the K2 Endpoint Service Type, represent a device-independent, cross-platform method of representing complex, relational data.
Service Authentication
The following Authentication Modes may be used with the Endpoints WCF Service Type:
- Impersonate
- OAuth
- ServiceAccount
- Single Single-on
- Static
Service Keys (Service Instance Configuration Settings)
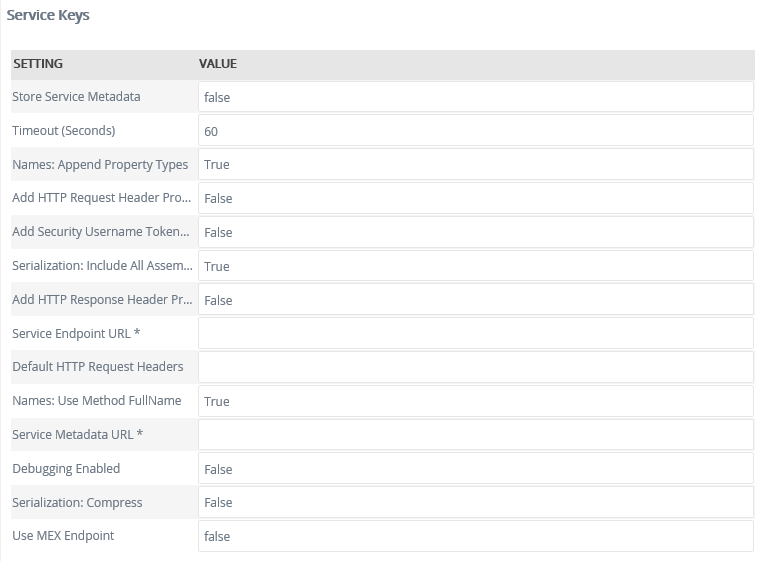
| Key | Can be modified | Data Type | Sample Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Store Service Metadata | Yes | True/False | False |
Sets the ability to store the service metadata of the WCF service. Default value: False. If this is set to true service metadata will be stored. For more information about using this field, see KB001602 Endpoint WCF Service / SmartObject fails when setting 'HTTPGetEnabled' to False. |
| Debugging Enabled | Yes | True/False | False | Displays stack trace information in dialog and error information. Default value: False.. |
| Names: Append Property Types | Yes | True/False | True | Includes the property type in parentheses after the complex property name. Default value: True. |
| Names: Use Method FullName | Yes | True/False | True | Uses the full name of the method including the property names and types. Default value: True. |
| Serialization: Compress | Yes | True/False | False | Compress the serialization data for complex types. Default value: False. |
| Serialization: Include All Assembly Types | Yes | True/False | True | Includes all available serialization objects regardless of usage in public methods. Default value: True. |
| Service Endpoint URL | Yes (required) |
Text | http://localhost/servicemodelsamples /service.svc |
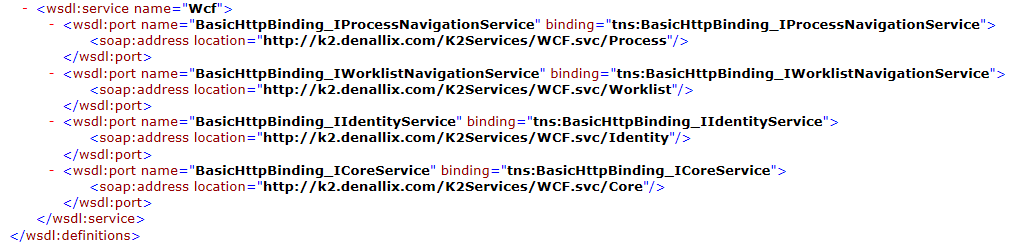
The URL to the service endpoint, typically the .svc address. If a service endpoint has multiple service bindings, such as the K2 Service WCF endpoint shown below, you must provide a service endpoint URL to a specific binding and register one service instance per binding. When you create your SmartObjects you can group them in the same category.
|
| Service Metadata URL | Yes (required) |
Text | http://localhost/servicemodelsamples /service.svc/mex | The URL to the service description (WSDL/MEX) for the Web Service. WSDL/MEX will automatically be appended if not found in the URL. |
| Use MEX Endpoint | Yes | True/False | False | The service description is provided as MEX instead of WSDL. Default value: False. |
Service Objects
When generating SmartObjects for an Endpoint Service Instance, some standard categories of SmartObjects are created; for example, the Object Types, and System Types. These define the data types used. Other SmartObjects may be generated depending on what the Endpoint exposes.

SmartObjects
K2 does not automatically create SmartObjects for the Service Objects in this service. SmartObjects are automatically created when selecting the Generate SmartObjects for this Service Instance check box when creating a new Service Instance. Designers may use the available Service Objects in this service to create advanced SmartObjects using the available K2 SmartObject design tools. It is recommended to use the K2 Design tools to create SmartObjects rather than generating SmartObjects, since this allows better control over the naming, behavior and design of the SmartObject and its methods and properties.
Considerations
- When working with EndPoint SmartObjects, an understanding of serialization and deserialization is essential. See Working with EndPoint SmartObjects for more information.
- For troubleshooting tips, please see Troubleshooting the EndPoint Service Types
- Changing WCF behavior, such as the maxReceivedMessageSize to address errors such as "The maximum message size quota for incoming messages has been exceeded” is accomplished by editing the K2HostServer.exe.Config file. (This particular error is common when many records are returned by the service)
- For more information about what is supported by the WCF service, see the Client Configuration topic on MSDN (http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms731745(v=vs.100).aspx). Make sure to use the right version of the article for the same .NET framework version that the K2 server is configured to run under.