See the introduction to K2 Pass-Through Authentication (K2PTA) in the Planning section.
The local group policy for each K2 Server Machine must be updated as per the following topic: Local Security Policy.
SharePoint Requirements
If the Client User's service call requires access to a specific database where K2 Pass-Through Authentication would be used, then the following user must be added to the database: NT AUTHORITY\ANONYMOUS LOGON.
K2 Pass-Through Authentication is installed with K2 blackpearl for all installations in a distributed environment. If a simple/full installation is chosen, K2PTA is not needed and you will not see the User Configuration page.
Along with the wizard-based configuration that is made while installing the system, settings are also located within the K2HostServer.exe.Config file using the DelegationContext node. The solution implemented (using these settings) determines how the system responds to and handles authentication errors.
Once these settings have been implemented, they are global for the K2 components, especially when K2 servers are load balanced. All nodes MUST have the same configuration to avoid inconsistent behavior.
The manner in which K2 Pass-Through Authentication works can be configured using the DelegationContext node in the AppSettings section of the K2HostServer.exe.Config file found in the ..\K2 blackpearl\HostServer\Bin\ folder. The two options for this setting are ClientKerberos and ClientWindows. This setting is global for all server connections regardless of the source. If a network load balancer (NLB) is in place, all K2 server nodes should have the same setting to prevent inconsistent behavior.
ClientKerberos
ClientKerberos is the default setting and the system will assume as much if no change is made. With this option set, the K2 server performs normal delegation using NTLM and assumes that Kerberos has been configured.
If Kerberos was not configured, error messages are logged in the K2 Server Log. When a connection is made that requests K2 Pass-Through Authentication, and delegation fails, an error message is logged to help identify the problem. When Kerberos Delegation or NTLM authentication takes place, the assumption is that the system is working as expected and no error messages are recorded.
ClientKerberos is the recommended option for enabling maximum security, which implies that the system administrator has decided not to use K2 Pass-Through Authentication. This is the recommended option due to the benefits of using Kerberos, such as better control of delegation and the passing of authentication requests. However, Kerberos introduces the requirement for good planning and a higher degree of expertise to install. Resources are available from the K2 Customer Portal to assist in configuring Kerberos, and it is strongly recommended that these be used.
ClientWindows
ClientWindows constrains K2 Pass-Through Authentication to only occur if the client credentials are of WindowsIdentity type (a valid Windows token). This implementation prevents less secure user clients such as Forms and Claims identities from passing credentials. If Kerberos (or NTLM) is working, it uses those credentials. This is the recommended option for environments containing only Windows users and who need to maximize functionality and security, and this does not require Kerberos to be configured.
When the K2 server runs in console mode, make sure to be logged in or use the K2 Server (Service Account) link to ensure that you're using the correct elevated privileges.
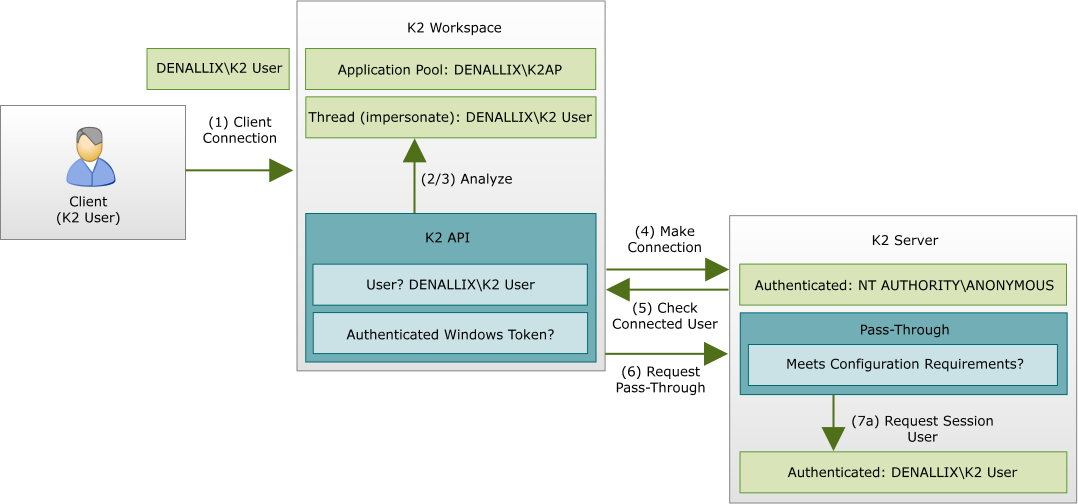
K2 Pass-Through Authentication follows a protocol which ensures that each valid authentication attempt is successful, regardless of the manner in which the K2 client APIs are used. This means that K2PTA functions as securely as possible.
The protocol follows the steps below:
- A client which may be a 'thick' (or lite) client e.g. K2 Workspace, makes a normal connection to the relevant K2 client API.
This initial connection is secure even for custom applications as it’s all conducted internally.
- The K2 client API analyzes the current configuration (e.g. user context and threads) to ascertain who is the intended end-user of the application.
- The user token is interrogated to ensure that it is a properly-authenticated Windows token
This process is to verify the ClientWindows configuration option.
- To initiate the process, a connection is made to the K2 server, just prior to K2 Pass-Through Authentication being performed.
- The relevant K2 client API asks the K2 Server which client was authenticated to determine if it’s different to the user calculated in step (2).
- If there is a difference, the K2 client API requests K2 Pass-Through Authentication, and then sends the K2 server the user’s name as well as passing in the result of (3).
- From the K2 server side, and depending on the requirements of the configuration option (e.g. ClientWindows):
- If step (6) is successful, the K2 server switches its security context from the current user (e.g. the anonymous user) to the K2PTA user.
- If unsuccessful, an error is logged due to the fact that there is a configuration issue on the client (because K2PTA failed). Any further functionality continues as the user (e.g. anonymous) as connected in step (4), including any connections to back-end systems.
When configurable levels of trust are required for each server on an individual basis in a distributed environment, Kerberos should be considered as this feature is beyond the scope of K2PTA and is the main strength of Kerberos, but does require additional configuration.