User Token Flow and Terminology
Claims and Active Directory User Tokens
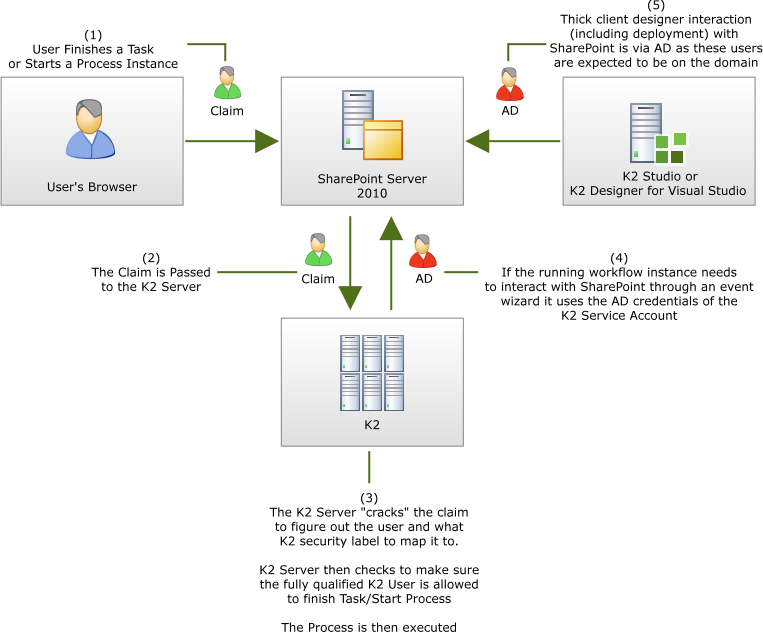
The following diagram illustrates the flow of claims based and Active Directory based user tokens in an environment configured with K2 and SharePoint 2010 claims based authentication.
Terminology
Claims Related Terms
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Claim | A statement that one subject makes about itself or another subject. For example, the statement can be about a name, identity, key, group, privilege, or capability. Claims have a provider that issues them, and they are given one or more values. This data about users is sent inside security tokens (SAML). |
| Claim rule | A rule that is written in the claim rule language of the provider that defines how to generate, transform, pass through, or filter claims. |
| Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) | A protocol that specifies how to use HTTP Web browser redirects to exchange assertions data. SAML tokens are XML representations of claims. |
| Identity Provider (IP) | A Web service that handles requests for trusted identity claims and issues SAML tokens. An identity provider uses a database called an identity store to store and manage identities and their associated attributes. |
| Relying Party (RP) | An application that consumes claims to make authentication and authorization decisions. For example, the K2 server receives claims that determine if the issuer user can access K2 data. |
| Claims-aware application | A relying party software application that uses claims to manage identity and access for users. |
| Security Token Store (STS) | A Web service that issues security tokens. SharePoint implements a STS to authorize activities within the application from multiple authentication providers |
| Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) | A protocol that improves the security of data communication by using a combination of data encryption, digital certificates, and public key cryptography. SSL enables authentication and increases data integrity and privacy over networks. SSL does not provide authorization or nonrepudiation. |
| Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) | A component of Windows Server 2008 that supports identity federation and Web single sign-on (SSO) for Web browser–based applications. |
| Federation server | A computer running Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2 that has been configured using the AD FS 2.0 Federation Server Configuration Wizard to act in the federation server role. A federation server issues tokens and serves as part of a Federation Service. |
| Federation Service | A logical instance of a security token service such as AD FS 2.0. |
SharePoint 2010 Terms
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Web Application Authentication Modes | |
| Classic Mode Authentication | Default mode. “Classic” Windows Authentication (NTLM, Negotiate (Kerberos)) and Anonymous support. |
| Claims Based Authentication (CBA) |
Support for non-Windows authentication. Ensures that all users are SAML token based for every Authentication Type. Note: SharePoint creates SAML 1.1 tokens for all authentication types. |
| Claims Authentication Types | |
| Windows Authentication (NTLM, Negotiate (Kerberos)) |
Negotiate (Kerberos) is the recommended security configuration to use with Windows authentication. If this option is selected and Kerberos is not configured, NTLM will be used. |
| Forms Based Authentication (FBA) | ASP.NET membership and role provider are used to enable Forms Based Authentication (FBA). |
| Trusted Identity Provider | Trusted Identity Provider Authentication enables federated users in this Web application. This authentication is Claims token based and the user is redirected to a login form for authentication. |
