3. Create Service Instances for External Data Sources; Generate SmartObjects
This application has two data sources that are external. The first data source (Azure SQL Service) provides a list of expense claim categories that you will use for a category drop-down list on the expense claim form. The second data source (Endpoint Web Services) has two functions: the first provides a list of currency codes that you will use for a drop-down list and the second converts the expense claim amount to US dollars. You can enter an expense claim item using another country's currency code and it is automatically converted to US dollars. This is especially helpful when entering travel expenses and eliminates the need to manually convert the amount yourself.
The first step when integrating with external systems such as SQL or web services, is to create a service instance. The service instance contains the connection configuration such as URL, server name, user name, password, and so forth. In this step, you will create a SQL Server service instance and an Endpoints Web Services service instance. You will also generate a SmartObject from the SQL Service service instance.
Creating a service instance allows K2 to discover the objects (such as the properties and methods) that the data source contains. Creating a SmartObject from the service instance allows K2 to interact with the data source through forms, workflows, and rules.
Service types, service brokers, and service instances are the elements that allow K2 to interact with other systems, and which form the base layer for SmartObjects. The following is a brief overview of each concept:
- Service Type: A service type is a pointer to a broker file for a specific system or data source. Examples include: SQL Server, SharePoint, CRM, and web services. Each service type has an underlying service broker associated with it.
- Service Broker: A file that contains the logic needed to interact with a specific system. Each service type has its own requirements for interacting with the system. For example, what type of authorization will the system allow? What type of data is contained in the system?
- Service Instance: A service instance is a single connection to a data source, and is based on the service type. The service instance uses the requirements defined by the broker to connect to the target data source. For example, you might have an instance of a SQL Server service type. The instance is specific to a single SQL database. If you have multiple databases, you need multiple instances. From the instances, you can then generate SmartObjects.
SmartObjects: The middle layer that allows interaction between a K2 object (form, view, workflow) and the target data source. For example, you have a form bound to a SQL SmartObject. When you submit the form, the SmartObject creates a new record or it updates an existing record in the SQL table. The SmartObject connects K2 to the system via the service layer.
-
Launch the K2 Management site.
- Launch the K2 Management site.If you are unsure of how to launch the K2 Management site, see Accessing K2 Sites.
- Launch the K2 Management site.
- Configure a new SQL Server Service Instance for the sample database that provides look-up values for expense categories. Use the table below for configure the service instance settings. If a setting is not specified, assume the default value.
Field Value Notes Service Instance A. Display Name K2 Tutorial SQL Database B. Description Service instance for the sample database used for K2 tutorials. C. Service Type SQL Server Service You will connect to a SQL database as the provider for this service instance. This is the connector used to connect to the target system. These connectors are also known as service types or service brokers and are usually technology-specific. Service Authentication D. Authentication Mode Static You will provide a static username and password to connect to the sample SQL database. E. User Name K2LearningUser F. Password K2LearningPass Extra (leave blank) Service Keys G. On Different SQL Server true The database exists on a physically different SQL server than your K2 system. H. Command Timeout 90 You want to extend the command timeout from the default to cater for high load. I. Database K2Learning This is the name of the target database on the target SQL server. J. Server uh8ydarb4m.database.windows.net This is the name of the SQL server you want to connect to. K. Use Native SQL Execution false You do not want K2 to use native SQL commands for this target database. It exists on a separate server and the K2 service account does not have enough permissions on the target system to perform DDL operations. SmartObjects L. Generate SmartObjects for this Service Instance UNCHECKED You will create the SmartObject after this step. - From the Management menu, expand the Integration node, then click Service Types. You will see current service types displayed in the central pane. Scroll through the service types until you locate SQL Server Service. You can also use the search option instead of scrolling through the pages. (You may see more than one search result returned.)
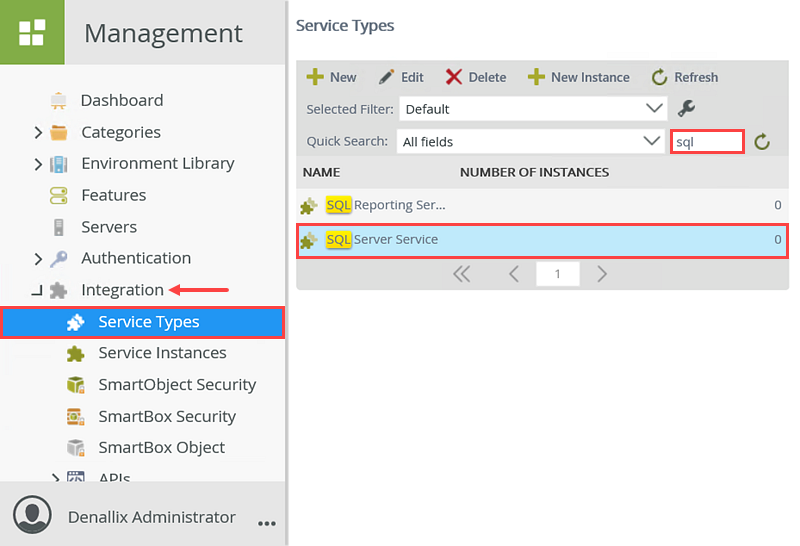
- Select SQL Server Service, then click the New Instance button in the toolbar.
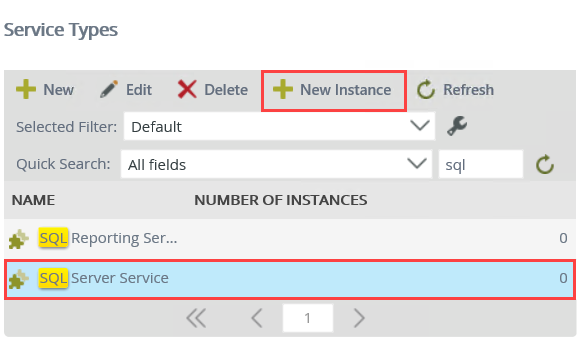
- Use the table below to configure the service instance. There is an image below the table to use as a reference, if needed. If a setting is not indicated in the table, assume the default value. Click OK when you have entered the configuration settings. Click OK for the confirmation dialog.
Field Value Notes Service Instance A. Display Name K2 Tutorial SQL Database B. Description Service instance for the sample database used for K2 tutorials. C. Service Type SQL Server Service You are connecting to a SQL database as the provider for this service instance. Connectors are also known as service types or service brokers. They are technology specific. Service Authentication D. Authentication Mode Static You will provide a static username and password to connect to the sample SQL database. E. User Name K2LearningUser F. Password K2LearningPass Extra (leave blank) Service Keys G. On Different SQL Server true The database exists on a physically different SQL server than your K2 system. H. Command Timeout 90 You want to extend the command timeout from the default to cater for high load. I. Database K2Learning This is the name of the target database on the target SQL server. J. Server uh8ydarb4m.database.windows.net This is the name of the SQL server you want to connect to. K. Use Native SQL execution false You do not want K2 to use native SQL commands for this target database since it exists on a separate server and the K2 service account does not have permissions on the target system to perform DDL operations. SmartObjects L. Generate SmartObjects for this Service Instance UNCHECKED You will create the SmartObject after this step. 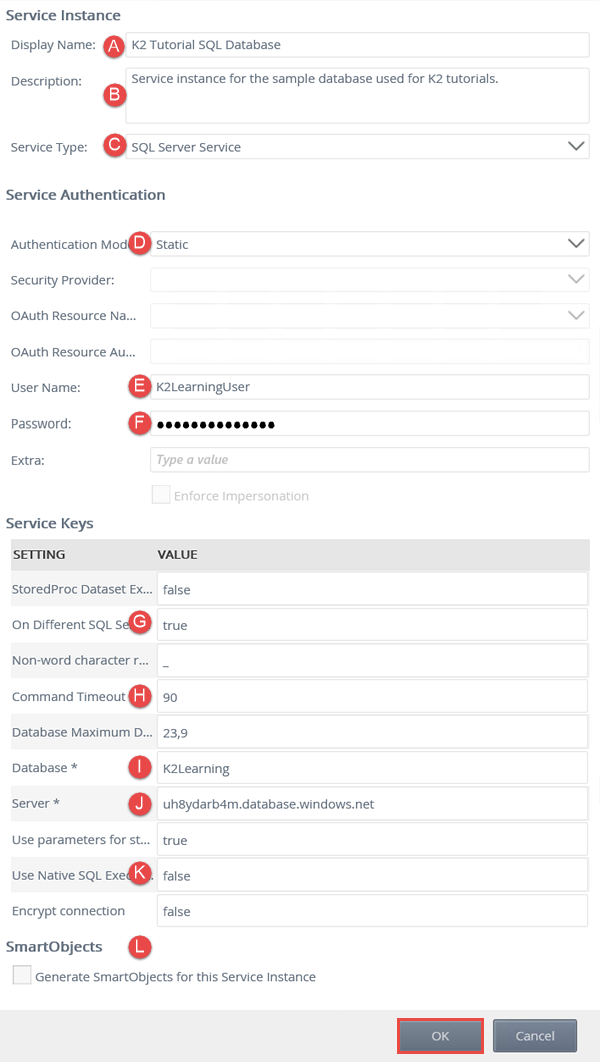
- From the Management menu, expand the Integration node, then click Service Types. You will see current service types displayed in the central pane. Scroll through the service types until you locate SQL Server Service. You can also use the search option instead of scrolling through the pages. (You may see more than one search result returned.)
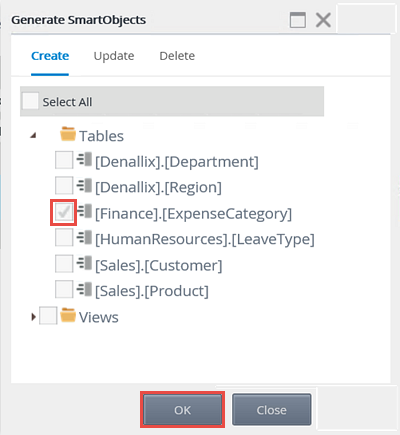
- Generate a SmartObject from the K2 Tutorial SQL Database service instance. Only select the [Finance].[ExpenseCategory] table.
- Next, you will create a SmartObject from the SQL Server Service instance. Creating a SmartObject exposes the properties and methods discovered in the data source, making them available for use in views, forms, and workflows. This particular SmartObject provides the look-up data for the expense claim categories drop-down list.
Still in the K2 Management site, expand the Integration node (if it isn't already), then click Service Instances. Navigate to (or search for) the K2 Tutorial SQL Database service instance. Click to highlight the service instance, then click the Generate SmartObjects button in the toolbar.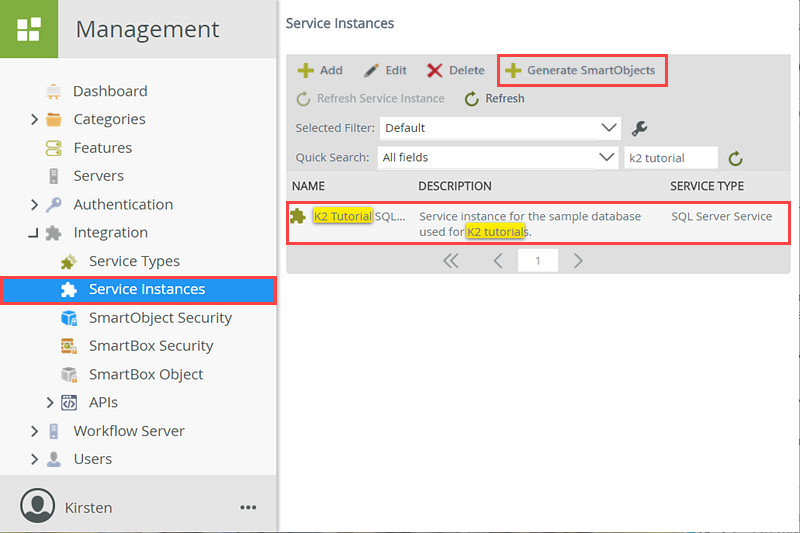
- On the Generate SmartObjects screen, expand the Tables node. (If the Tables and/or Views nodes are already checked, uncheck them first. You don't need to create SmartObjects from all the tables and views, you will be selecting a single table from which to create the SmartObject.) CHECK the [Finance].[ExpenseCategory] table, then click OK.

- Next, you will create a SmartObject from the SQL Server Service instance. Creating a SmartObject exposes the properties and methods discovered in the data source, making them available for use in views, forms, and workflows. This particular SmartObject provides the look-up data for the expense claim categories drop-down list.
-
From the K2 Management site, execute the new SmartObject's list method and confirm expense category results are returned.
- Next, you will test the SmartObject to confirm the connection configuration from the service instance is valid.
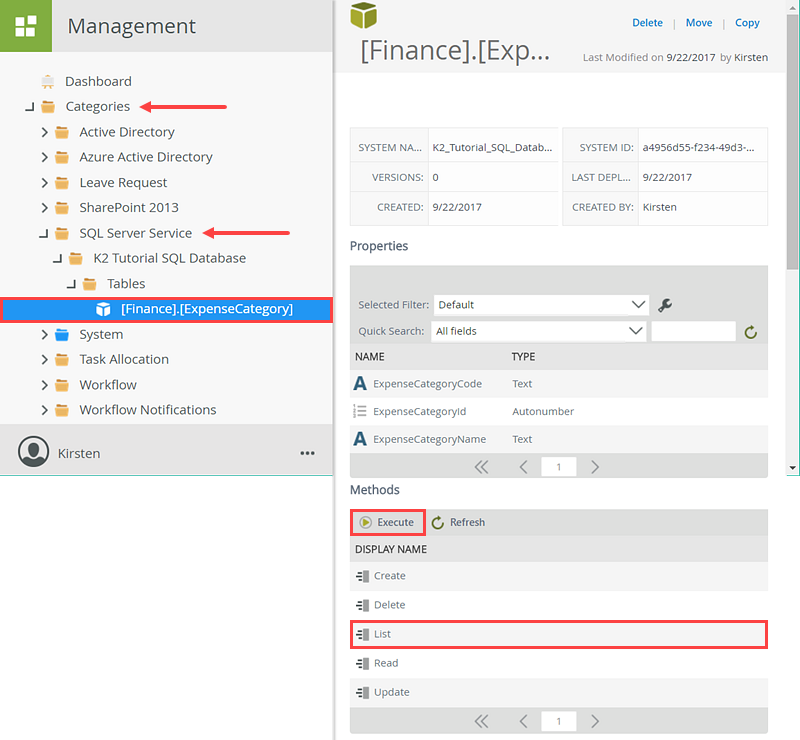
In the Management menu, expand the Categories node. Expand the SQL Server Service > K2 Tutorial SQL Database > Tables nodes. Click the [Finance].[ExpenseCategory] SmartObject. The SmartObject details, properties and methods opens in the central pane. Scroll down to the Methods section. Select the List method, then click Execute.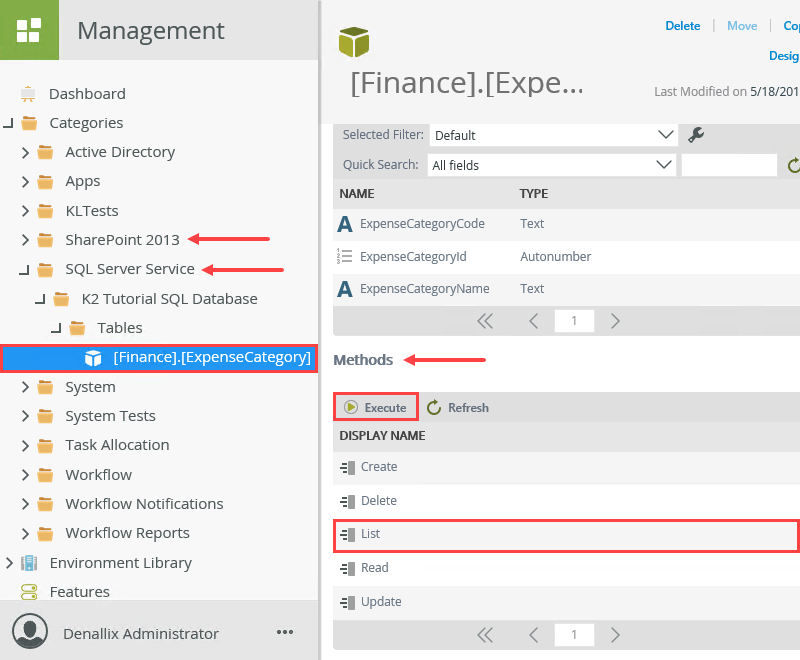
- Click the Execute button in the lower right corner of the screen. You will see results displayed the same screen, which confirm the connection. This data source provides the drop-down list values for the expense categories. Click Done to close the screen.
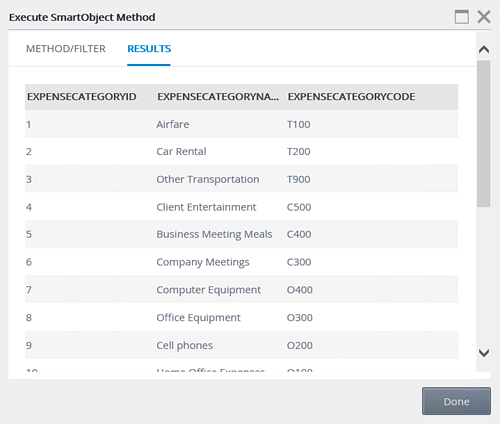
The Execute SmartObject Method screen opens. Here, you can apply filters before executing the method. In some cases, such as read methods, you must provide input parameters before executing the method. For this test, you just want to confirm the connection, so you don't need any filters.
- Next, you will test the SmartObject to confirm the connection configuration from the service instance is valid.
-
Create a second service instance using the Endpoints WebService service type. Use the table below as a guide for the service instance configuration:
This web service is for tutorial purposes only. Do not use this web service for production environments. The web service used by this application also runs on Azure. This web service should be accessible through port 80 and unless your organization has strict firewall policies in place, it should be available for use anywhere. If you need to host the web service internally, you can download the source code for the web service from the following location: http://help.k2.com/files/8554. Contact a member of your application development team for help, if necessary.
Field Value Notes Service Instance A. Display Name K2 Tutorial Currency Web Service B. Description Service instance for the sample currency web service used for K2 tutorials. C. Service Type Endpoints WebService Service Authentication D. Authentication Mode ServiceAccount You will use the credentials of the K2 service account to connect to the target web service. When using the service account authentication mode, the service account must have the necessary permissions to interact with the data source. Be aware of this when registering a new service instance in your own environment. Service Keys
There is only one service key value to set in this step (WebService URL).E. WebService URL http://k2learning.azurewebsites.net/ExchangeRates.asmx This is the URL of the target web service you will connect to. F. Generate SmartObjects for this Service Instance UNCHECKED You will manually create a SmartObject in a later step. - Next, you will add another service instance which points to a web service that you will use for currency conversion operations.
Open a new browser window and verify you can connect to the following web service:
http://k2learning.azurewebsites.net/ExchangeRates.asmx
You should see a screen similar to the image below.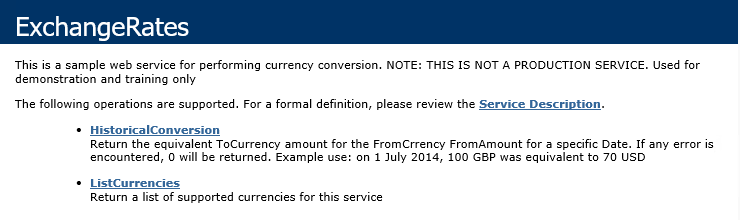 This web service is for tutorial purposes only. Do not use this web service for production environments. The web service used by this application also runs on Azure. This web service should be accessible through port 80 and unless your organization has strict firewall policies in place, it should be available for use anywhere. If you need to host the web service internally, you can download the source code for the web service from the following location: http://help.k2.com/files/8554. Contact a member of your application development team, if necessary.
This web service is for tutorial purposes only. Do not use this web service for production environments. The web service used by this application also runs on Azure. This web service should be accessible through port 80 and unless your organization has strict firewall policies in place, it should be available for use anywhere. If you need to host the web service internally, you can download the source code for the web service from the following location: http://help.k2.com/files/8554. Contact a member of your application development team, if necessary. - Returning to the K2 Management site, expand the Integration node, then click on Service Types. Scroll down to (or search for) the Endpoints WebService. Click to highlight the Endpoints WebService, then click the New Instance button in the toolbar.
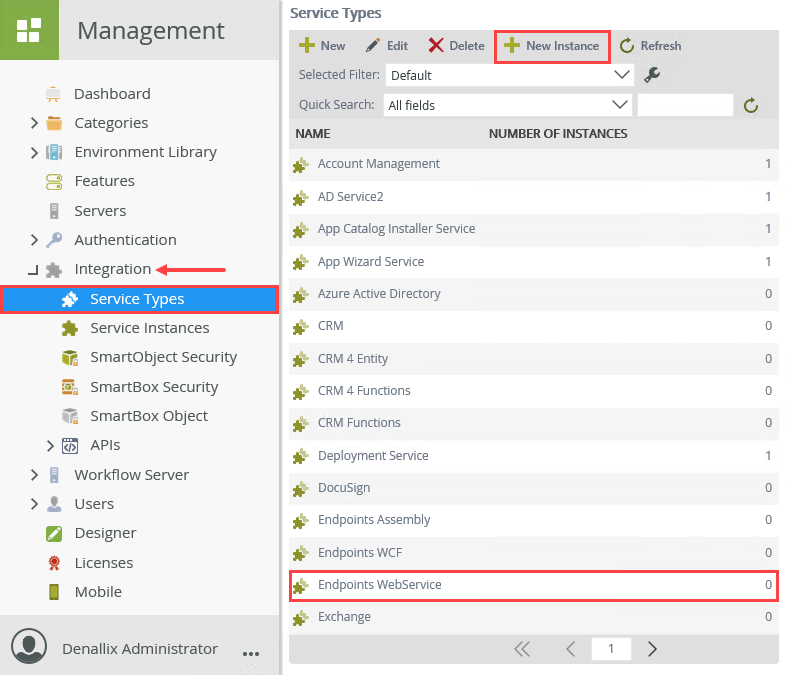
- Use the table below to configure the service instance. There is an image below the table to use as a reference, if needed. If a setting is not indicated in the table, assume the default value. Click OK when you have entered the configuration settings. Click OK for the confirmation dialog.
Field Value Notes Service Instance A. Display Name K2 Tutorial Currency Web Service B. Description Service instance for the sample currency web service used for K2 tutorials. C. Service Type Endpoints WebService Service Authentication D. Authentication Mode ServiceAccount You will use the credentials of the K2 service account to connect to the target web service. When using the service account authentication mode, the service account must have the necessary permissions to interact with the data source. Be aware of this when registering a new service instance in your own environment. Service Keys
There is only one service key value to set in this step (WebService URL).E. WebService URL http://k2learning.azurewebsites.net/ExchangeRates.asmx This is the URL of the target web service you will connect to. F. Generate SmartObjects for this Service Instance UNCHECKED You will manually create a SmartObject in a later step. 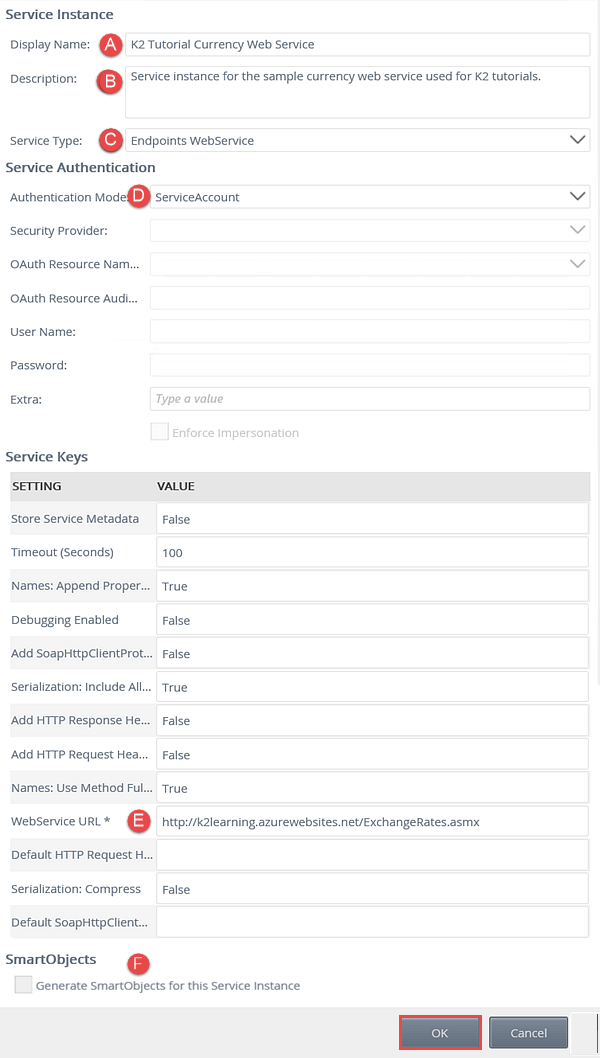
- Still in the Integration node, click Service Instances. Confirm you can see both new service instances: K2 Tutorial Currency Web Service and K2 Tutorial SQL Database. Your external data connections are ready for use!

- Next, you will add another service instance which points to a web service that you will use for currency conversion operations.
Review
In this step, you created two service instances for external data sources. The first data source is an Azure SQL database, while the second data source is a web service. The SQL data source provides the drop-down list values for expense categories. The web service provides values for currency conversion and currency listings. You generated a SmartObject from the SQL Server service instance, selecting the single expense category table. For the currency SmartObject, you will create a new SmartObject from scratch using K2 Designer. In the next step, you generate application elements from the Expense Claim list. This creates the base artifacts for the expense claim application: views, forms, and reports.